Most discussions about artificial intelligence in healthcare focus on clinical breakthroughs, but the largest near-term gains come from administrative operations that affect revenue and patient satisfaction. Administrative AI programs can reduce back-office workloads while improving claim accuracy and efficiency.
For engineering and platform leaders, AI in healthcare is a delivery accelerator. By automating prior authorization triage, coding, and scheduling, advanced healthcare systems reduce costs and free staff to focus on patient care.
Deploying administrative AI often delivers measurable ROI within six months when implemented on event-driven architecture and with strict review thresholds. Prioritize operational AI now, as it pays off first. Clinical AI can follow.
The real opportunity lies in disciplined integration: secure data pipelines, auditable AI models, and human-in-the-loop (HITL) oversight that enable compliance and reliable service delivery. Responsible use of AI systems in compliance programs enables scalable and predictable outcomes.
Context: Why Administrative AI Deserves Your Focus
In 2026, most healthcare organizations face staff shortages and rising complexity in billing, scheduling, and compliance. As a result, the healthcare industry is adopting AI technology to alleviate manual backlogs while protecting patient safety.
Machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) applied to electronic health records reveal inefficiencies, predict denials, and surface missing documentation while ensuring data integration. This secure flow of data across departments creates smoother handoffs and fewer errors. Insights from McKinsey confirm measurable improvements in operational throughput, extending to clinical practice and support functions that reinforce patient care.
AI models can identify patterns in claims data to reduce denials and improve throughput. Administrative AI also simplifies referrals and billing. The opportunity is to optimize administrative workflows without touching direct clinical practice.
Where Administrative AI Fits and Where It Doesn’t
High-impact use cases combine structured data with human checkpoints:
- Prior authorization triage: AI extracts criteria, flags gaps, and pre-populates forms for review.
- Medical coding assistance: AI maps notes to codes, boosting throughput with human validation.
- Denial prediction: Machine learning flags claims likely to be denied for correction before submission.
- Scheduling optimization: Algorithms match provider availability, utilization, and expected no-shows.
- Patient flow routing: Real-time AI optimizes bed assignments and discharge timing to improve patient outcomes.
Clinical decision support and medical diagnosis remain out of scope. These require validation under FDA AI/ML medical device guidance (December 2024 final guidance; January 2025 draft update) and oversight involving medical professionals. Research areas such as clinical trial monitoring and early detection also depend on more mature regulatory frameworks.
AI Integration Patterns That Actually Work
Successful AI adoption depends less on the model and more on integration with existing healthcare delivery systems.
Event-driven interfaces connect EHR and RCM through queues or HL7 FHIR APIs, providing standardized resource models and transport for safe data exchange across electronic health records.
Minimal PHI exposure is essential: redact unnecessary fields before inference, ensure encryption, and enforce access controls compliant with HHS HIPAA security standards.
Using OpenTelemetry or similar frameworks, teams can correlate AI activity with performance metrics and audit events. Interoperability based on HL7 FHIR or ASC X12N 837 healthcare claim standards ensures consistency and scalability.
Virtual assistants can also improve intake efficiency and reduce documentation friction. AI tools built for administrative efficiency increasingly integrate with electronic health records to enhance patient safety and clinical workflows.
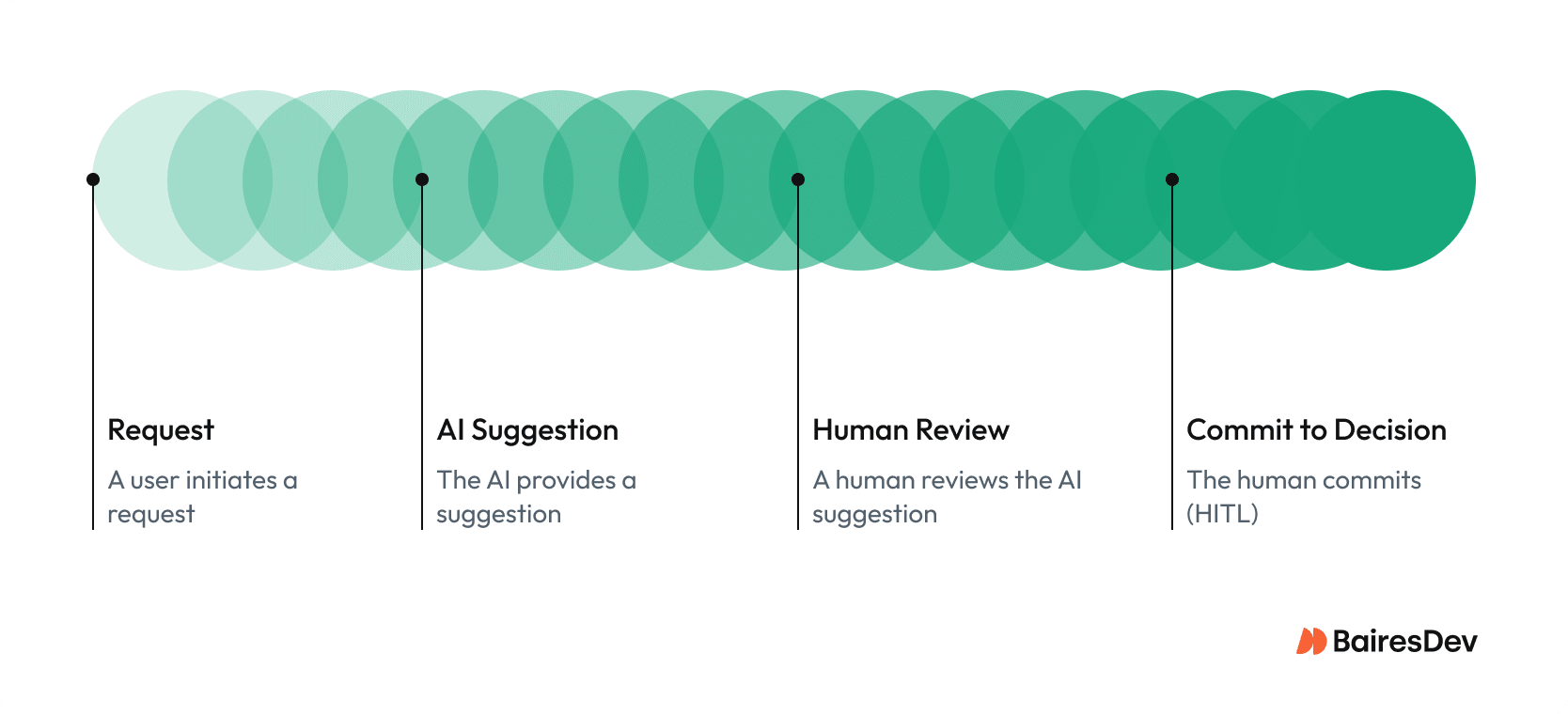
Human-in-the-Loop and Safety-by-Design
Automation without oversight creates risk. Safe AI adoption combines automation with human expertise.
Confidence thresholds define automation levels, routing results to human review where needed. Role-based queues let coders and schedulers work efficiently within defined risk bands. Dashboards track latency and exception volumes as measurable service objectives, while regular simulation and bias testing ensure fairness and prevent over-automation.
These controls turn opaque systems into transparent workflows. Every inference can be traced from data source to final decision, satisfying both regulators and healthcare professionals.
Virtual assistants support administrative staff by managing routing tasks or surfacing patient-specific data within oversight boundaries. Human review ensures reliability and improves compliance.
Measuring Value and Realizing ROI
Executives measure results through outcomes, not model metrics. Let’s examine the impact of AI on operations, finance, and user experience.
| Level | Example Metric | Source System |
| Operational | Coding turnaround time, queue age, no-show rate | EHR, RCM |
| Financial | Denial rate, days in A/R, clean-claim percentage | Billing |
| Experience | Staff rework rate, satisfaction score, average handle time | HRIS, call center |
What about the risks?
According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, healthcare data breaches averaged $9.77 million in 2024, a 10.6% decrease from 2023’s $10.93 million. Proper governance and encryption of health data protect both revenue and reputation.
The healthcare industry’s breach exposure remains the highest across sectors, as tracked by the HIPAA Journal.
Run-State Governance and SLOs
AI services require production-grade reliability and accountability.
- Latency below 2 seconds for 95% of requests, accuracy ≥ 90%, and queue backlog under 15 minutes.
- Incident handling follows NIST SP 800-61 Rev.3 (April 2025 release). Failures trigger review and documentation.
Organizations that incorporate AI and automation into their security processes saw breach costs $2.2 million lower on average than those that did not, according to IBM’s findings.
Good governance is a productivity multiplier. Treat it as an urgent priority. Enforcing accountability fast-tracks AI adoption while addressing ethical concerns and safeguarding data. Well-governed frameworks ensure reliable results and audit readiness.
AI Governance and Compliance Alignment
Effective AI adoption requires governance aligned with national security and privacy standards. Frameworks such as the NIST AI Risk Management Framework and ONC Trusted Exchange Framework (TEFCA) help healthcare systems integrate AI solutions safely into compliance programs.
Engineering leaders should embed AI checkpoints directly into audit cycles, tying data lineage, model drift monitoring, and incident logs to HIPAA-required access reviews and retention policies. By combining observability with regulatory reporting, teams can manage AI models like any other system of record.
Well-governed AI in healthcare creates stronger documentation trails for certification and reduces breach exposure through automated evidence collection. Integrating these controls strengthens confidence among payers and regulators while building accountability across healthcare organizations.
Talent and Operating Model
Sustainable AI adoption depends on process and culture. Cross-functional pods manage delivery, with training ensuring every reviewer understands AI models and exception workflows.
Standing up an AI Center of Excellence can accelerate ROI and governance maturity, as supported by industry analyses noting that dedicated AI governance structures improve operational consistency and oversight.
Prioritization Framework for AI Investment
Most organizations prioritize projects that combine clear data sources with visible financial return.
| Use Case | Integration Complexity | Key Dependency | Typical ROI Window |
| Denial Prediction | Low | Claims feed | 3–4 months |
| Coding Assist | Medium | NLP model + RCM API | 4–6 months |
| Scheduling Optimization | Medium-High | EHR calendar + OR data | 6–9 months |
| Prior Auth Triage | High | Multi-system interfaces | 9–12 months |
Organizations that integrate AI early can see measurable gains in revenue stability, staff retention, and other metrics. Industry surveys, including HIMSS-affiliated reports, indicate that healthcare organizations using AI-driven revenue-cycle automation have reduced claim denials by up to 30%.
Impact on Healthcare Providers and Clinical Practice
By reducing documentation bottlenecks, AI gives medical professionals more time to focus on patient care and good service. While clinical practice remains human-led, administrative automation reduces friction between departments and complements personalized medicine initiatives.
Studies show AI-enabled coding can reduce errors by 20–50% and lower claim denials by 20–30%. Clean data and efficient workflows improve downstream clinical data as well. As AI improves clinical trial design and outcome prediction, these programs gain strength.
Business Impact and ROI Model
Administrative AI yields four compounding benefits:
- Cost reduction: less rework and faster claim resolution.
- Throughput gains: improved bed utilization and discharge speed.
- Staff efficiency: healthcare professionals focus on higher-value work.
- Audit readiness: embedded logs simplify compliance with HHS and ONC privacy rules.
Industry surveys show healthcare organizations using AI-driven revenue-cycle automation are seeing a reduction in claim denials and shorter turnaround times. Automating pre-submission validation avoids payer penalties and supports better patient outcomes.
What “Good” Looks Like
Mature AI technology behaves like any reliable production service.
- Each inference is logged with reviewer and model version.
- Dashboards show latency, accuracy, and exceptions.
- Rollback paths are tested monthly.
- Encryption and redaction routines are validated quarterly.
- Feedback loops continuously retrain AI algorithms to improve accuracy.
Each inference should remain verifiable within its clinical context to ensure safety and accountability. Healthcare AI systems demonstrate maturity when they achieve stable, observable performance across all metrics.
Implementation Realities: Time, Cost, Ownership
Here’s what implementation typically looks like in practice: a short discovery phase, a controlled pilot, a governed rollout, then steady-state operations. Most organizations reach production readiness in ~4–6 months.
| Phase | Duration | Core Activities | Primary Owner |
| Discovery | 4–6 weeks | Data inventory, risk assessment, baseline metrics | Platform + Ops |
| Pilot | 6–8 weeks | Shadow testing, KPI tracking, model tuning | Data/ML |
| Rollout | 8–12 weeks | Human-review deployment, monitoring setup | Platform |
| Steady State | Ongoing | Retraining, audits, quarterly governance | Compliance + Ops |
Typical annual cost: $100K–$300K for infrastructure, plus two engineers and training support. Compared with losses from denials or data breaches, this is a modest investment in long-term stability for healthcare providers.
Strategic Takeaways
Administrative AI succeeds when it’s treated like infrastructure, not experimentation.
- Treat administrative AI as a platform capability with SLOs.
- Governance and data protection enable scale.
- Start with RCM use cases closest to revenue.
- Align engineering and operations for continuous AI adoption.
AI programs that follow these constraints reach steady state faster and survive audits without disruption.
BairesDev’s Perspective
At BairesDev, we approach AI in healthcare the same way we approach platform engineering. If it can’t be monitored, audited, and owned in production, it doesn’t ship.
Our teams work with healthcare organizations to integrate AI into existing EHR and revenue-cycle systems, define review thresholds, and build evidence trails that stand up to audits. This results in measurable reductions in denial backlogs, faster scheduling turnaround, and fewer operational escalations during compliance reviews.
What differentiates successful programs isn’t the model. It’s disciplined integration, clear ownership, and treating AI as part of the core delivery platform rather than a standalone initiative.
Future Outlook: Where AI in Healthcare Is Headed
The next wave of artificial intelligence in healthcare will emphasize interoperability and privacy-preserving innovation. Approaches like federated learning enable models to train across distributed electronic health data without moving protected information.
AI tools will increasingly support precision medicine, drug discovery, and personalized treatment, bridging operational and clinical domains. AI is also improving clinical trial design and monitoring, predicting outcomes, and enhancing early detection capabilities. Emerging applications include interpreting medical imagery and supporting diagnostic workflows for chronic diseases.
Research from the National Bureau of Economic Research estimates that wider adoption of AI could save between $200 billion to $360 billion annually in U.S. healthcare spending. But savings are just part of the equation. By combining engineering discipline with mature AI systems, healthcare institutions also build trust. In healthcare, trust is what determines whether AI remains a pilot, or becomes infrastructure that clinicians and patients will actually adopt and rely on.






