You’re paying a senior engineer six figures to copy-paste data.
They’re manually triaging support tickets, pulling nightly reports, or babysitting a brittle deployment script written by someone who left the company two years ago. It’s a soul-crushing waste of your most expensive talent and a massive drag on your entire delivery engine. It’s killing morale.
This isn’t a people problem. It’s a systems problem. It’s why we need to have a serious conversation about hyperautomation.
Long-term forecasts project the market for hyperautomation will hit $1 trillion by 2026, and it’s not a fad.
Let’s be blunt. Most automation efforts are like giving one person a power drill. It’s useful, but it doesn’t fundamentally change how you work. You’re still relying on heroic individuals.
Why Hyperautomation Matters to Technology Leaders
Hyperautomation is different. It’s about designing and building the entire automated assembly line.
Think of it as an operating system for your business. It’s not one tool; it’s a framework that orchestrates multiple technologies to handle a process from end to end. It goes beyond the simple, rule-based tasks of traditional automation. A real hyperautomation system:
- Uses Process Mining to find the real bottlenecks.
It watches how your teams actually work, not how the flowchart says they work, to find the true sources of delay and toil. - Orchestrates a whole toolbox.
It’s not just Robotic Process Automation (RPA). It’s RPA handing off to a Machine Learning (ML) model for a decision, which then uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read a PDF, and then logs the outcome in your ERP via an API call. A Business Process Management (BPM) layer acts as the conductor for this whole orchestra. - Handles the messy reality.
The real world isn’t structured. Hyperautomation is designed to ingest unstructured data, like the text of a customer email or the scan of an invoice, and turn it into structured actions. - Creates a feedback loop.
The system doesn’t just run; it provides data on its own performance. You get dashboards showing cycle times, exception rates, and throughput, so you can continuously improve the process instead of just letting it run in the dark.
This isn’t about automating a single task. It’s about fundamentally re-architecting your workflows so they are scalable, resilient, and no longer dependent on burning out your best people.
“This sounds a lot like automation,” you might be thinking. And in some way, it is.
Hyperautomation essentially boils down to automation at scale. It aims to automate nearly all repeatable business and IT processes.
How Hyperautomation Goes Beyond Traditional Automation
Traditional automation often means scripting isolated tasks. Hyperautomation scales that up:
- Coordinates tools across departments
- Continuously identifies automation opportunities
- Handles exceptions and unstructured data
- Links into enterprise systems (ERP, CRM, data lakes)
It’s the difference between automating one process and shifting to an automation-first operating model.
Core Technologies Powering Hyperautomation
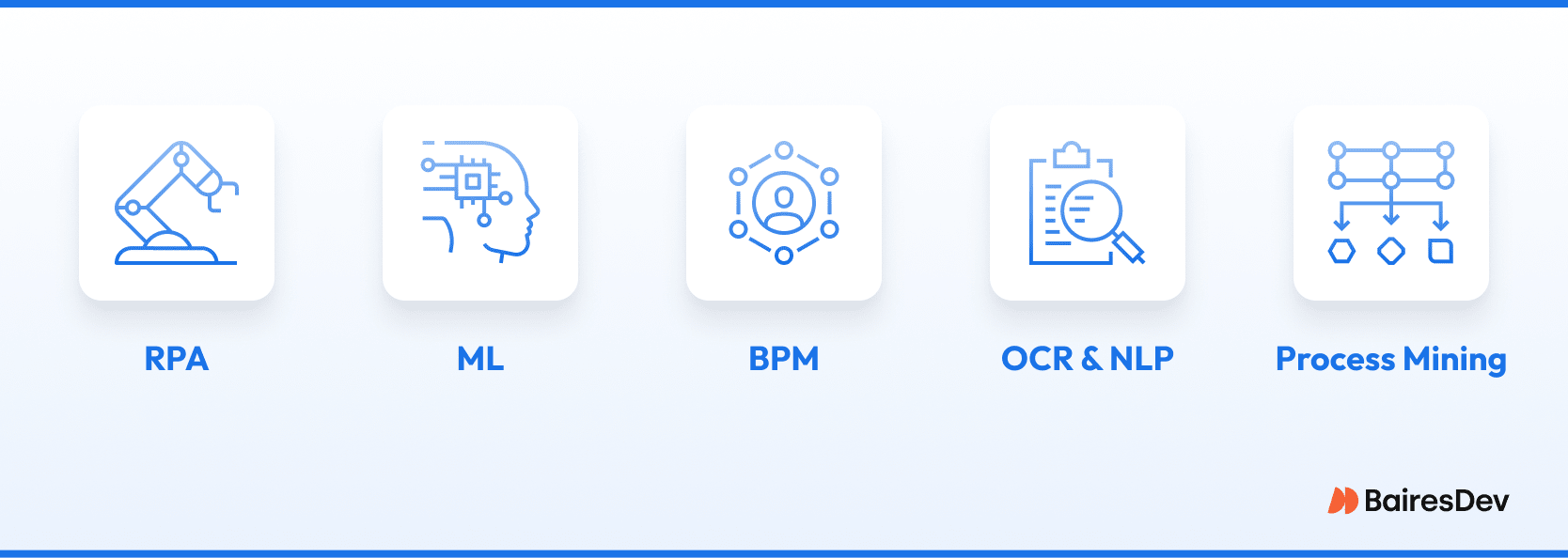
- RPA (Robot Process Automation): Automates rule-based, repetitive tasks
- ML (Machine Learning): Extracts insights from structured and unstructured data
- BPM (Business Process Management): Orchestrates processes across tools and teams
- OCR & NLP: Handle documents, forms, and emails
- Process Mining: Identifies automation candidates and tracks improvement
Tools and Technologies in Robotic Process Automation
Robot process automation (RPA) sits at the core of hyperautomation, which involves the orchestrated use of multiple technologies. This technology follows assigned rules and completes tasks that are generally repetitive and rote.
RPA can’t learn or perform highly complex tasks, which is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) come into play.
Augmented by these more advanced tools, which can understand patterns, the technologies can work in conjunction to perform tasks that humans previously performed — and far more quickly, too. Combing through unstructured data sets, advanced technologies can automate tasks crucial to business operations.
RPA, AI, and ML aren’t the only technologies involved in the hyperautomation process. It also leverages business process management, big data, and advanced analytics to simulate human intelligence and perform responsibilities without being explicitly “told” to do so.
Why Should You Consider Implementing Hyperautomation?
By 2025, hyperautomation is expected to optimize operations across various industries, including finance, customer service, and logistics, resulting in a significant reduction of manual labor and operational inefficiencies.
Tight budgets and aggressive delivery goals? Hyperautomation may be the answer as it:
- Improves speed and accuracy
- Frees up internal bandwidth
- Reduces operational risk
- Supports digital transformation goals
Enterprise Benefits at a Glance
Enterprise clients often realize significant ROI within 6–12 months of implementation. They should expect:
- Faster cycle times and throughput
- Fewer manual errors
- Scalable, repeatable workflows
- Better audit readiness
- Improved employee productivity
A typical use case of hyperautomation could be found in the insurance industry, where it’s used to streamline end-to-end claims processing workflow. Traditionally, claims handling was slow, and processing a single claim could take several days to complete. After implementing the process automation, manual effort could be reduced by as much as 40%.
How to Actually Implement Hyperautomation: A Practical Playbook
Your first move is the most important, because it’s where most companies get this wrong. They try to create a grand, top-down “hyperautomation strategy.” They spend six months in meetings, produce a 50-page slide deck, and build nothing.
Find the Pain, Not the ‘Potential’
Stop looking for “opportunities for automation.” You’ll get a list of 100 things and drown in analysis paralysis.
Instead, find the most acute, recurring pain. Walk out of your office and go talk to your head of Finance, Ops, or Customer Support. Ask them a simple question: “What mind-numbing, repetitive task is burning out your team the most?”
They will know exactly what it is.
You’re listening for things like: “My team spends the last three days of every month manually reconciling thousands of transactions just to close the books.” Or, “We have to manually process 500 return authorizations a week, and every single one is touched by three different people.”
Look for high volume, high drudgery, and a high error rate. That’s your target.
Baseline Everything, in Dollars and Hours
If you can’t measure it, you can’t sell it to the CFO. Before you touch a single tool, you need to quantify the pain. Answer these questions with hard numbers:
- Human Cost: How many people are involved in this process? How many hours per week, total, do they spend on it?
- Financial Cost: What is the fully-loaded cost of that time? Get a real number, get the annual cost of toil.
- Error Cost: What is the current error rate? What is the business impact of those errors? Rework, shipping delays, angry customers, compliance risks?
Put this on a single page. This document is your business case. It’s not for you or your team. It’s for the people who approve your budget.
Launch a 90-Day Pilot
Again, you are not building a “platform.” You are not creating a “center of excellence.” You are launching a single, fast, visible pilot project that solves the one painful problem you identified.
This is a “tracer bullet”—a narrow, end-to-end implementation that proves the entire system works and delivers undeniable value. Your goal for this pilot must be a single, unambiguous metric. For example: “Reduce the manual effort for invoice processing by 80% and cut the cycle time from 72 hours to 8 hours, within one quarter.”
You focus all your energy on hitting that one number. You integrate the necessary automation tools for this one process only. You are proving value, not boiling the ocean.
Use the Data to Justify Scaling.
Your successful pilot isn’t the end. It’s the ammunition you need to win the war, to tie your efforts to business outcomes.
Now you go back to that one-page business case. You update it with the “after” state. You walk into the executive meeting and say:
“Our pilot for invoice processing is live. We invested $X. We are now saving the company an estimated $Y per year in labor costs and have eliminated data-entry errors, which we estimate saves us another $Z in rework. It will deliver a 3x ROI in the first year. Here are the next five high-pain, high-ROI processes I’ve identified. I need a budget of $W to assemble a small, dedicated team to tackle these over the next six months.”
That’s how you get it done. You don’t ask for permission to “explore a strategy.” You rapidly identify opportunities and show decision-makers the money you’ve already saved them and a clear plan to save more.
Industry Applications
- Finance & Insurance: Automated reconciliations, policy issuance, risk scoring. ML helps flag anomalies or claims exceptions. Automations cut cycle times and reduce error rates.
- Healthcare & Pharma: Claims intake, patient onboarding, compliance workflows. OCR + ML automates document ingestion. BPM tracks handoffs from admin to medical reviewers.
- Manufacturing & Logistics: Predictive maintenance alerts based on sensor data; automated procurement requests; inventory stock reconciliation. Reduces downtime and supply delays.
- Retail & e‑Commerce: Order-processing, returns handling, customer inquiry triage. ML classifies inquiries, RPA routes transactions, BPM ensures SLA compliance.
Across these sectors, hyperautomation reduces manual workload, accelerates cycle time, and improves customer or partner experience.
Common Challenges and How to Mitigate Them
Hyperautomation introduces complexity by combining multiple automation tools that we’ve discussed. This often leads to workflow silos and system conflicts.
“Automating chaos just gives you faster chaos,” as one industry expert puts it. A major issue is data inconsistency and poor integration, especially with legacy systems. Many teams automate broken processes, which can actually make things worse.
To avoid this, start with clear process mapping and focus on standardization. “Fix existing processes before you automate,” is a common rule. Without strong governance, projects stall or disrupt operations. Assign ownership, manage change carefully, and audit regularly.
A phased rollout helps maintain control and scale effectively.
Maintenance of Your Strategy
Maintaining a hyperautomation strategy requires ongoing attention to stay effective and aligned with business goals. As tools evolve and processes shift, regular updates and oversight become essential.
Think of incorporating these practices:
- Monitoring and evaluating: Continuously monitor and evaluate automation efforts to ensure they meet business objectives and make adjustments as needed.
- Providing training and support: Provide training and support to business users to ensure they can effectively use automation technologies.
- Addressing data quality issues: Address data quality issues to ensure that automated processes are accurate and reliable.
- Continuously monitoring and improving: Continuously monitor and improve automation processes to ensure they remain effective and efficient.
Will Hyperautomation Replace Humans?
No—but it will change roles.
Repetitive, low-value tasks will shift to bots. That frees your teams to focus on oversight and optimization.
In high-volume operations, this improves both employee engagement and process reliability.
There is a certain amount of fear surrounding the use of automation. AI, in particular, has some people thinking that technology will make human skills obsolete.
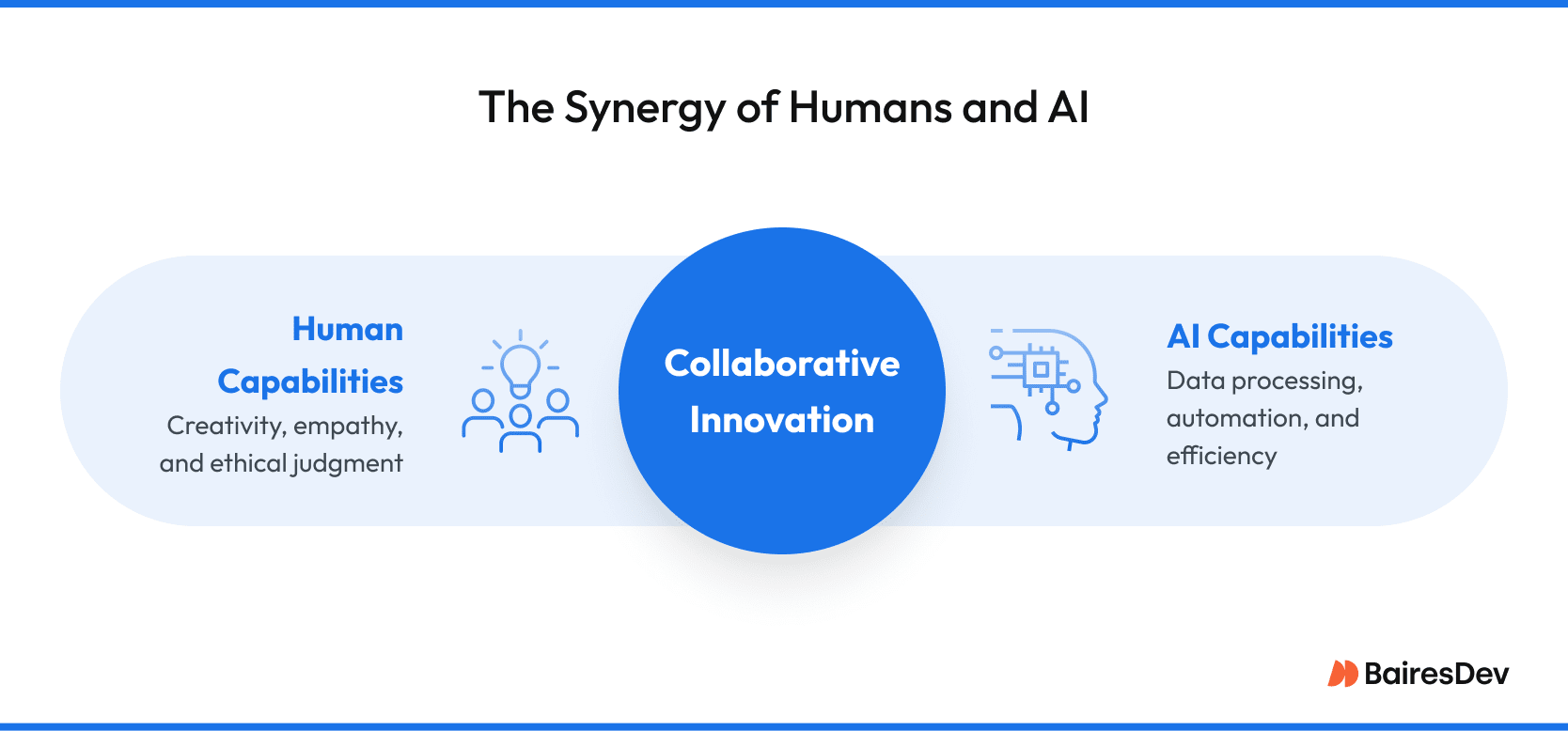
However, hyperautomation software wasn’t conceptualized as a tool to replace humans altogether. Instead, it’s intended to become a means of collaboration.
Future of Hyperautomation – 2026 and Beyond
The future of hyperautomation is exciting – we can expect to see even more sophisticated and intelligent automation solutions emerge.
Additionally, the use of intelligent optical character recognition and process mining will enable organizations to streamline workflows effectively.
Expect these key trends:
- Agentic automation agents will be executing decisions autonomously by 2028, though firms must be cautious to avoid “agent washing” or mislabelling conventional AI as agentic
- Edge‑enabled automation where IoT sensors feed ML models, triggering RPA actions—for example, in manufacturing or logistics.
- Explainable AI in pipelines to meet governance, compliance, and risk requirements—especially in regulated industries.
- Human‑machine collaboration models where BPM dashboards guide engineers and business users in oversight and refinement.
Your Next Move: From Toil to Throughput
Hyperautomation isn’t just about trimming expenses—that’s a side effect. The real prize is building a new operational engine for your business. It’s about creating scalable throughput and declaring war on the repetitive, manual toil that burns out your best engineers and grinds your delivery engine to a halt. It’s a fundamental change to how you operate.
Inevitably, the conversation turns to platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Microsoft Power Automate. They are all powerful, and your choice will likely depend more on your existing tech stack than a minor feature difference. But fixating on the tool is a rookie mistake. A powerful platform doesn’t find the business pain for you, design the workflow, or build the business case. Your strategy and your execution are what determine success or failure, not the logo on the software.
Trying to build this capability from scratch is risky. This isn’t a side project you can hand to your platform team; it requires a specific blend of process architecture and data engineering that most teams don’t have on the bench. Getting that first pilot project wrong is incredibly costly. You don’t just waste budget, you lose the political capital and trust needed to try again.
This is why leaders bring in specialists. A partner like BairesDev provides the experienced engineering teams who have built these automated assembly lines before. We help you execute that critical first 90-day pilot, deliver an undeniable ROI, and build the momentum you need to scale. The first move is to stop analyzing and start building.