Emerging cyber threats move faster than most teams can react. Technology leaders need strategies to detect and block attacks early, keep workflows moving, and protect delivery schedules without compromising cyber security.
Is Your Cybersecurity Playbook Obsolete?
Even well-tested security playbooks can lose their edge quickly in 2026. Threats now shift faster than gradual updates or standard planning can manage. Frameworks that aren’t tailored and aligned with the culture and processes lead to failure.
Adversaries use automation and AI to probe networks, identify weak points, and launch attacks in hours. Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report found that critical systems are compromised in less than an hour. Faster than most organizations and cybersecurity professionals can respond. Worse, the average time to discover a breach is 200 to 300 days.
Playbooks built on fixed steps cannot adapt to dynamic, multi-pronged campaigns. Procedures that depend on manual handoffs or hierarchical approval layers introduce delays that attackers exploit. Staying resilient means using live intelligence, automating response, and learning from each incident.
Emerging Cyber Threats and Enterprise Risk
Enterprise defenses that fail to evolve will struggle against the broader array of attack paths emerging in 2026. Seeing these cyber threats clearly is the first step to deciding where to invest resources.
Fortinet’s 2025 Global Threat Landscape Report reveals that organized cybercrime groups use automated scanning on a massive scale — up to 36,000 scans per second. On the dark web, initial access brokers trade stolen logins, VPN credentials, and admin panels. Ransomware crews and state-sponsored threat actors move quickly. Every partner, system, and identity can be pulled into the conflict.
Attackers concentrate on weak spots where defenses haven’t kept up. Identity systems, supply chains, open-source software, and even national infrastructure are all in play.
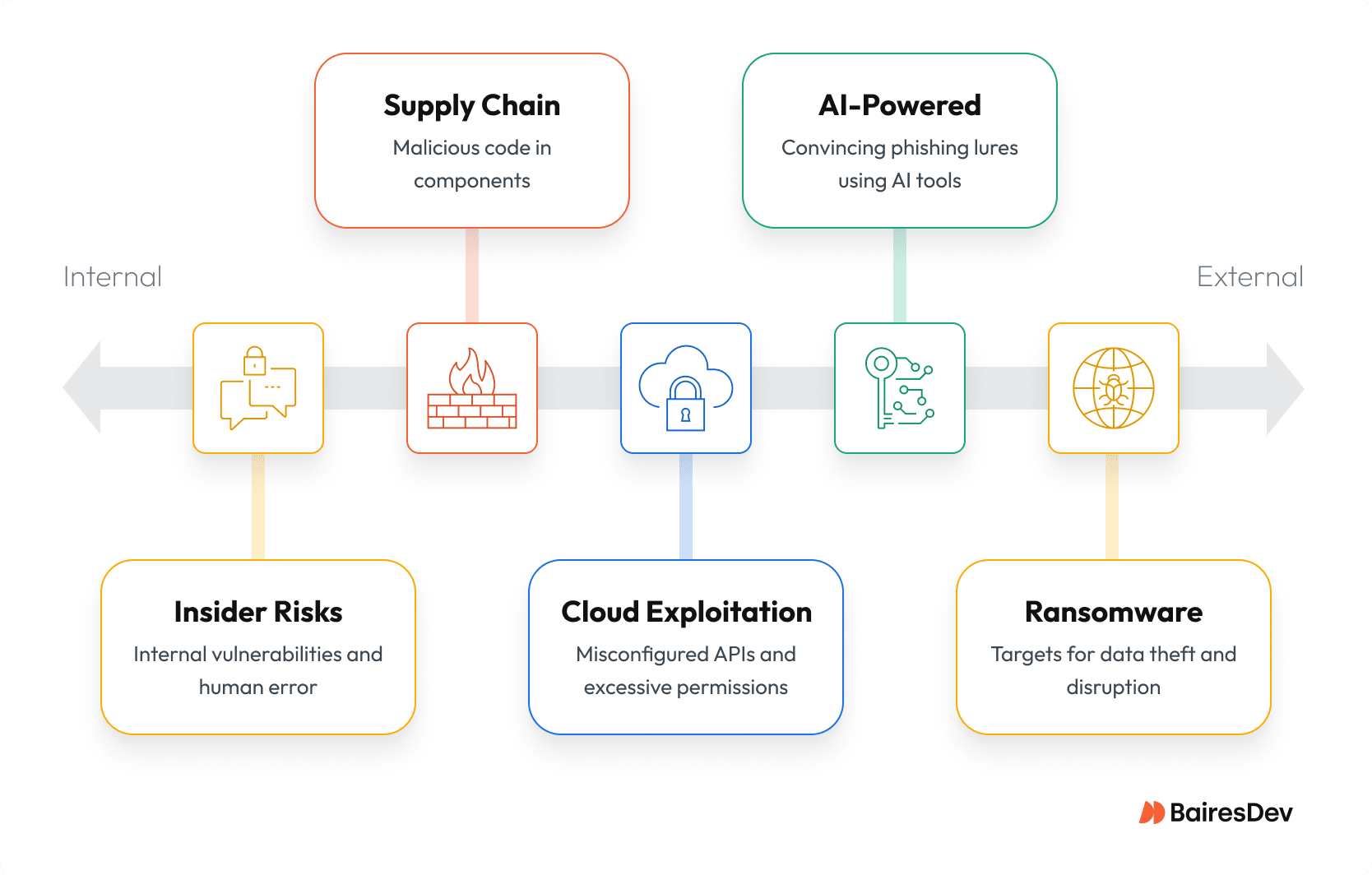
The top threats teams face include:
- AI-powered social engineering: Adversaries craft more convincing phishing lures and malicious code using widely available AI writing tools. Low-barrier image-generation AI enables them to craft realistic deepfakes. These lures are harder to train against and often slip past traditional filters.
- Supply chain compromises: Access brokers sell stolen credentials and VPN logins on the dark web. Intruders inject malicious code into build steps or third-party components. Unpatched open-source packages give attackers an early advantage before fixes are released. A single compromise can spread silently through CI/CD pipelines.
- Cloud and identity exploitation: Misconfigured APIs, excessive permissions, and login abuse from unusual geographies provide adversaries with easier points of entry. Once inside, intruders can move across cloud and on-prem systems, causing downtime and outages.
- Ransomware and nation-state threats: State-backed groups and fragmented ransomware crews infiltrate targets for data theft, disruption, or long-term surveillance with advanced persistent threats. Their campaigns cause costly incident response and may undermine national security.
- Insider threats: Not every breach starts outside the perimeter. MFA fatigue — where attackers inundate users with repeated login prompts until one is approved — combined with shadow IT, unsanctioned AI use, and insider mistakes, creates vulnerabilities. The fallout can be compliance violations, outages, or damaging leaks.
Table: Top 5 Emerging Cyber Threats in 2026 and Delivery Impact
| Emerging Threat | Description | Delivery Impact |
| AI-Driven Social Engineering | AI-driven tools enable phishing, deepfakes, and synthetic voice lures that bypass training and filters. | Employee compromise spreads malware, delays projects, and disrupts workflows. |
| Supply Chain Compromise | Stolen credentials, unpatched open-source packages, and compromised CI/CD pipelines are sold by dark web brokers or exploited directly. | Weak links cascade through CI/CD pipelines, delaying releases or fueling ransomware incidents that halt operations. |
| Cloud & Identity Exploitation | MFA fatigue, misconfigured APIs, broad permissions, and login anomalies give attackers easy entry into cloud systems. | Downtime, compliance delays, and outages disrupt service availability and delivery schedules. |
| Ransomware & Nation-State Threats | Fragmented ransomware groups and state-backed actors target manufacturing, government, and critical infrastructure. | Service outages, production stoppages, and costly incident response cycles stall enterprise delivery. |
| Insider Threats | Shadow IT, unsanctioned AI use, and employee mistakes create vulnerabilities that perimeter defenses miss. | Compliance violations, outages, or insider-driven leaks derail projects, service delivery, and credibility. |
Shadow AI and Insider Threats
Shadow AI is a new vulnerability. Chances are your developers already use unsanctioned AI tools. These shortcuts bypass secure code reviews and controls, risking insecure code and sensitive data leaks.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report found that 20 percent of breaches involved the use of shadow AI, often when developers pasted sensitive snippets into external tools. These incidents exposed customer PII and intellectual property. The report also notes that the rise of shadow AI displaced the security skills shortage as one of the top three costly breach factors.
Shadow AI demands clear policies and education to balance speed and productivity. Left unchecked, it can lead to compliance gaps, insecure code in production, or missing documentation that auditors will flag. All this is expensive to fix downstream.
Threats Posed to Delivery and Uptime
Cyber threats hit delivery hard. IBM found that while the global average breach cost fell to $4.44 million, U.S. costs surged to a record $10.22 million. For tech leaders, the cost is measured in downtime, missed deadlines, and lost credibility. The cost of a breach doesn’t paint the full picture, as it doesn’t account for the indirect costs of security breaches.
Incidents routinely trigger project delays, operational outages, and disrupt operations. A single breach can cascade through CI/CD pipelines, cloud platforms, and vendor networks, creating a business-wide crisis.
CI/CD and DevOps Environments
Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are the backbone of modern software delivery, but their automation and speed make them prime targets. A compromise in DevOps can cause customer-facing outages and trust issues. The most critical risks include:
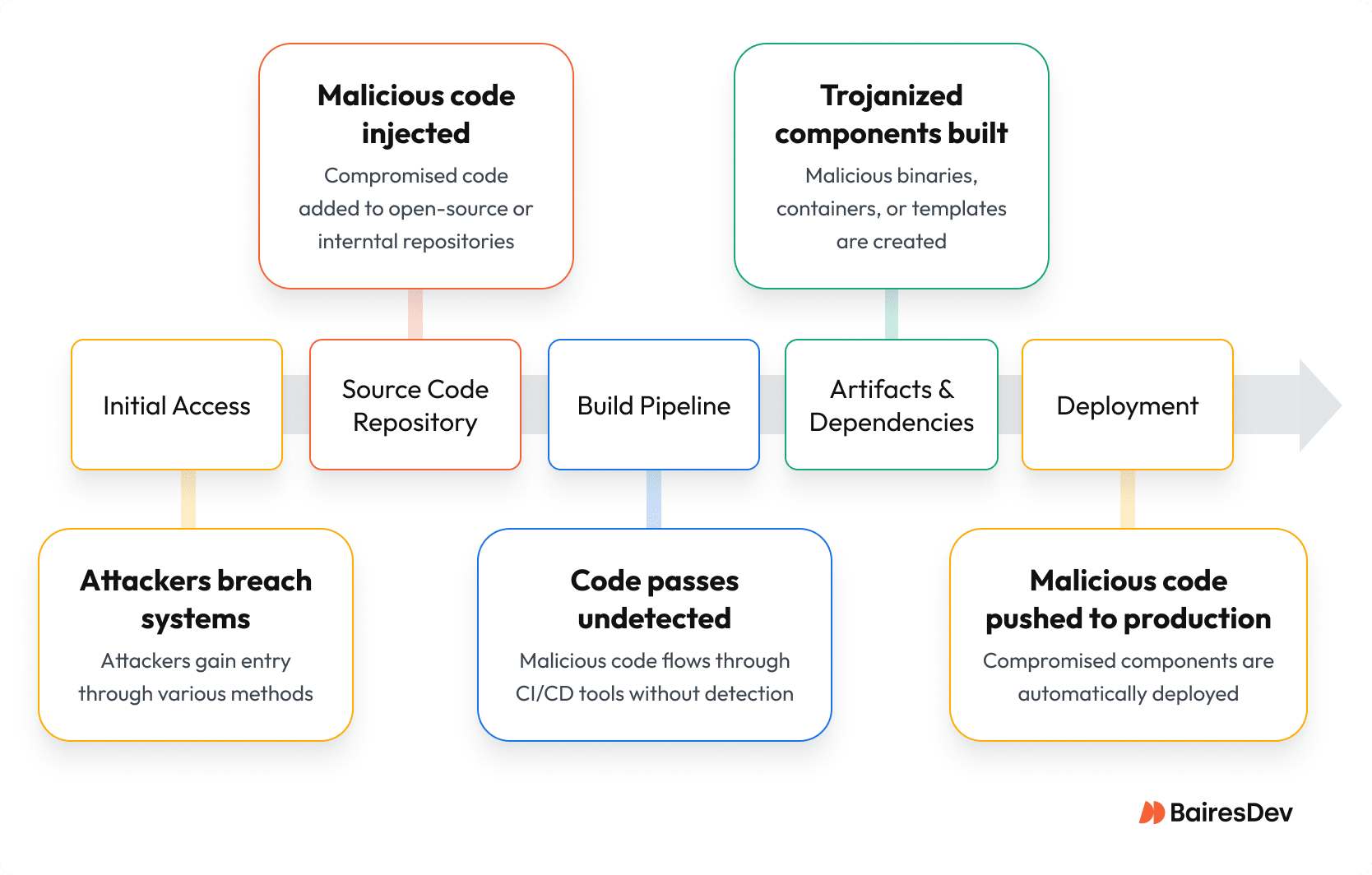
- Malicious code injection: Attackers embed code in source repositories or dependencies, poisoning build artifacts before deployment. Automated pipelines accelerate the spread, pushing compromised builds into production before security teams can catch them. This vector is addressed by integrating security scanning and DevSecOps with hard gating.
- Compromised developer credentials: Stolen developer credentials give adversaries a foothold. With elevated access, they can alter build processes, escalate privileges, and quietly derail release schedules.
- Persistent threats in CI/CD pipelines: Once inside, adversaries chain together insecure APIs, misconfigurations, and identity weaknesses to maintain persistence. If someone owns your CI/CD, they own your source code and can do anything.
Cloud and Edge Threats
Cloud and edge platforms give enterprises scale, but they also widen the attack surface. Misconfigured services, over-permissioned roles, and weak identity controls continue to open the door for adversaries.
Fortinet’s 2025 Global Threat Landscape Report calls out cloud as a principal battleground, with attackers blending persistence and credential abuse into everyday operations. The top risks in these environments include:
- Cloud identity abuse: Fortinet’s research reveals that, in 70 percent of documented cloud identity compromises, attackers logged in from unexpected geographic locations.
- Workload and container compromises: Trojanized or vulnerable container images can introduce malware directly into production. Cryptojacking campaigns are also on the rise, hijacking compute resources under the guise of regular DevOps activity.
- Edge vulnerabilities: As more workloads move closer to users and BYOD policies expand, edge devices have become even more attractive targets. Limited physical security, inconsistent patching and decentralized deployment make them a perfect target for infiltration.
Adversaries aren’t breaking in. They’re logging in. That shift makes cloud-focused detection and defense a top priority for enterprise security teams.
Operational Downtime and Financial Impact
Cyber incidents rarely stop at a technical failure. They slow delivery, inflate costs, and erode customer trust. Outages across global supply chains break SLA commitments, while recovery efforts pull resources from core priorities.
IBM reports that the average time to identify and contain a breach fell to 241 days, a nine-year low attributed to the adoption of AI and automation-driven defenses. Verizon found that 46 percent of breaches involved third parties or supply chain partners. When upstream vendors are compromised, delivery schedules slip, recovery grows more complex, and overall costs rise sharply.
How a Supply Chain Attack Propagates Through CI/CD
CI/CD pipelines automate deployment, so a compromise can propagate malicious code from development to production in minutes, turning speed into risk.
Resilient Cyber Defenses for the Modern Enterprise
Building resilience involves expecting disruption, maintaining real-time visibility, and stress-testing defenses against AI-driven threats.
Zero Trust as a Security Foundation
Zero Trust assumes no user, device, or service, inside or outside the network, is trusted by default. Every access request must be verified, and permissions are limited to the bare minimum.
The core Zero Trust principles include:
- Assume breach, verify access: Segment networks and apply layered controls under the assumption that an intruder is already present. Encrypt data end-to-end and use analytics for pattern visibility.
- Least privilege access: Users and systems get only the access required for their role or task. Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Access (JIT/JEA) methods reduce exposure and help protect confidentiality.
- Continuous verification: Monitor active sessions for anomalies and re-authorize when risk signals appear. Trust is earned in real time, not granted once.
Zero Trust is more than a compliance checkbox. It’s a scalable defense for hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Implementation often starts with MFA, identity and access management (IAM), microsegmentation, and endpoint security.
For more mature models, you extend protection to APIs, SaaS platforms, and partner integrations. The focus should be on integrating telemetry, and the core value is integrated analysis and insights. The goal of zero value is to stop lateral movement, preventing intruders from spreading once they are inside.
Build for Resilience
Assume failure will happen and plan for rapid recovery. Resilience stems from layered controls, redundant infrastructure, disciplined patching, and the validation of disaster recovery plans.
Backup validation and failover testing are critical frontline defenses. Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs 2025 forecasts warn that ransomware crews build wiper malware into their payloads, permanently destroying data instead of encrypting it. These destructive tactics make recovery without tested, redundant backups nearly impossible.
IBM’s data indicates that tested backups, continuous monitoring, and layered defenses cut breach costs by an average of $1.5 million compared to unprepared teams.
Other effective strategies include:
- Software Bills of Materials (SBOMs): An SBOM inventories every software component, including versions, licenses, and known vulnerabilities. Having an SBOM shortens response times when a flaw or supply chain compromise is disclosed.
- Real-world testing: Regular red-team, purple-team, and tabletop exercises expose process and communication gaps.
- Continuous monitoring and exposure management: Real-time telemetry across cloud, endpoints, and networks reduces detection times, so you’re ready for faster remediation. Exposure monitoring extends this by validating what attackers could exploit, providing a prioritized, attacker’s-eye view of risk.
Threat Modeling for Proactive Defense
Threat modeling helps you view your environment from the perspective of an attacker. By mapping systems, data flows, and user roles, you rank risks and close off attack paths before they’re exploited.
The most effective threat-modeling practices include:
- Business-aligned modeling: Focus on the systems and data that matter most. Protecting high-value assets first ensures you place resources where your business impact is greatest.
- Continuous updates: Your threat models must evolve with the environment. New integrations, hybrid cloud adoption, and AI-driven attack tactics can shift how adversaries move.
- Attack path simulation: Automated breach-and-attack simulation (BAS) tools stress test defenses against realistic attack scenarios and TTPs.
A 2025 World Economic Forum white paper on balancing the risk and reward of AI in cybersecurity adds that pairing these measures with AI-enhanced threat modeling and continuous validation helps reduce detection times and costly misconfigurations.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) gives enterprises a way to track exposures as they change, not just during point-in-time tests. It supplies you with a running view of where attackers could get in.
Fortinet’s research shows exposure management is one of the fastest-growing defensive practices. Organizations are adopting CTEM to push past reactive patching and have near-real-time visibility into their attack surface. The most valuable CTEM features include:
- Ongoing validation: Continuous scans surface exposed assets, misconfigurations, and unpatched vulnerabilities as they appear.
- Prioritization: CTEM tools rank exposures by exploitability and business impact so your team fixes the issues most likely to matter first.
- Business integration: Exposures are mapped to enterprise assets and delivery workflows, linking technical flaws directly to delivery and uptime risk.
Offshore and Nearshore Security and Compliance
Distributed teams accelerate delivery and expand capacity. But this model can also introduce cross-border security and compliance challenges.
As operations grow, you need a proactive approach to protect sensitive data, navigate regulatory differences, and maintain trust.
Secure Collaboration
Distributed teams present more opportunities for credential theft or sensitive information leaks if access controls are not correctly tuned. Your zero-trust safeguards must be strong enough to block intruders, yet flexible enough for daily work to continue.
The World Economic Forum found that companies pairing identity governance with MFA and AI-driven, context-aware monitoring cut unauthorized access incidents by nearly 50 percent.
Regional Governance, Risk, and Compliance Requirements
When data moves across borders, it faces regulatory conflicts, interception risks, and mishandling. Consistent standards across regions, mapped to your GRC requirements, let distributed teams work securely without creating compliance blind spots or slowing nearshore operations.
For U.S. federal contracts, all operations must comply with NIST Special Publication 800-171, and increasingly, the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) Program certification levels when handling controlled unclassified information. The most effective safeguards include:
- Encryption: Protect data in transit and at rest to guard against interception or unauthorized access.
- Controls and logging: Apply role-based permissions and maintain detailed audit logs to limit exposure and ensure traceability during investigations.
- Data residency and lawful transfer: Define policies for where data is stored and use frameworks such as the GDPR Standard Contractual Clauses to uphold lawful transfers across jurisdictions.
Third-Party and Vendor Risk Management
Large organizations often rely on subcontractors and service providers, which creates shared responsibility for protecting data. Without clear policies, these links can become weak points that adversaries exploit.
According to IBM, supply chain and third-party breaches averaged $4.91 million per incident. Costs that underscore why a rigorous vendor risk program is as critical as your own internal defenses.
Effective safeguards include:
- Vulnerability disclosures: Require software vendors to provide SBOMs and commit to transparent vulnerability disclosure practices.
- Security certifications: Vet vendors against standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, or CMMC to confirm baseline security maturity.
- Right-to-audit clauses: Include audit rights in contracts to verify that vendors maintain the required controls and compliance obligations.
Distributed Team Security Checklist
Use the following checklist to help secure engagements and operationalize these practices:
- Require MFA and identity governance across all accounts.
- Encrypt files, communications, and data transfers end-to-end.
- Align outsourced operations with your compliance frameworks.
- Document cross-border data handling policies and enforce encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit.
- Vet vendors and subcontractors for security certifications, SBOMs, and disclosure practices.
- Add right-to-audit clauses in all contracts.
- Monitor your networks for unusual activity across remote and cross-border access points.
- Perform quarterly vendor risk assessments and security audits.
- Insert contractual SLAs requiring 24–48 hr breach notification from vendors.
Staying Ahead of Evolving Threats Actors
Attackers innovate daily. Organizations that adapt the fastest, through skilled teams, intelligence-led processes, and organizational agility, gain the upper hand. To stay ahead, you must invest in people and culture that evolve as fast as the threat landscape.
Security teams require ongoing training to keep pace with new TTPs and AI-driven threats. Certifications, scenario testing, and intelligence-sharing networks all sharpen defenses while also improving retention in a market where cybersecurity talent shortages remain an issue.
- Threat modeling and attack simulation: Teams that model attack paths and run breach-and-attack simulations uncover gaps before attackers can exploit them. These exercises sharpen technical proficiency and validate defenses against real-world scenarios.
- AI-powered detection and response: Leveraging AI-driven tools, such as SIEM, XDR, and automated triage systems, enables your analysts to cut through noise, reduce intruder dwell time, and focus on high-value investigations.
- Intelligence collaboration: Fusion centers and Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) give teams early insight into attacker tactics. Pooling intelligence helps teams adjust defenses before campaigns scale.
Building Confidence Against the Latest Cyber Threats
AI-powered, organized, and automated adversaries attack with ingenuity and speed that scales. Enterprise leaders require flexible strategies, modern tools, and skilled personnel who can adapt to the evolving cyber threats.
As a trusted nearshore software development and staff augmentation partner, BairesDev provides enterprise-ready engineering talent, secure DevOps practices, and innovative AI skillsets. We can help you defend critical systems, stay ahead of attackers, and deliver without compromise.






