You spent two years in the indie grind, coding late nights in your pixelated hoodie. Then came the Unity pricing switch. It blindsided game developers who just wanted to ship great games. The runtime fee dropped like a Unity-bombed patch note. Install counts were changed into debt. And while the fee was canceled, scars remain.
Unity CEO John Riccitiello called it “moving gaming forward.” Devs called it something else. The fear of seat creep still hangs over new and existing Unity projects, and it’s even worse for Unity personal games built without big studio budgets.
Maybe you survived the first wave? Maybe you flew under the qualifying annual revenue thresholds. Unity enterprise customers are back to more traditional prices. Even so, many indie game devs still wonder if Unity’s next update will add features or fees.
What Is the Unity Pricing Controversy?
The Unity pricing issue started in 2023, when CEO John Riccitiello announced a new runtime fee policy that made a big change to game development costs. The new model would charge game developers every time someone installed their game. It kicked in after a specific total annual revenue and install threshold.
The change blindsided the industry, sending fee shock zapping through Reddit’s /r/gamedev and the indie community.
Backlash
Anger spiked up online. Prominent voices like Rami Ismail called out the new prices. Forums and developers at GDC questioned Unity’s metrics, sparking install-count paranoia in the game development industry.
The problem was the way Unity engine tracking would work. Developers were afraid of “ghost installs.” These were fees paid for pirated copies or updates that didn’t come with any revenue. The policy risked punishing Unity personal games and small shops. Meanwhile, big Unity enterprise customers got better deals. It felt like a dev tax on success.
Reversal and Reality
With so many angry developers, Unity backpedaled in 2024. The company scrapped the runtime fee and replaced it with more traditional cycle price hikes and a minimum subscription requirement. As of January 1, 2025, existing Unity Pro and Unity Enterprise users pay higher seat costs.
Under the new terms, game developers pay based on subscription tiers like Unity Pro. The price is determined by total annual revenue and team size. Unity also promised to discuss customized packages for larger studios. They committed to improve game development transparency, too. While the dust has settled, many developers are still wary. The Unity splash screen still reminds them that their trust was pulverized overnight.
But the real shock is the numbers. Ironically, the raw numbers in a Unity pricing example (below) don’t show a disaster. They show how perception and unpredictability caused more damage than the actual cost. In other words, the pricing model wasn’t always financially devastating. But it was opaque, unstable, and threatening. That was the real cost.
Real Costs: What a 250K-Install Indie Game Would’ve Paid
Under the proposed fee, a typical Unity indie title with 250,000 installs and $1.25M in revenue would’ve paid about $10K. In the revamped subscription model, Unity Personal users pay nothing. By comparison, Unreal’s 5% fee over $1M meant a $12.5K hit. For tight-budget teams, that margin mattered. But as the example below shows, real revenue didn’t change all that much for many.
Revenue Comparison Table
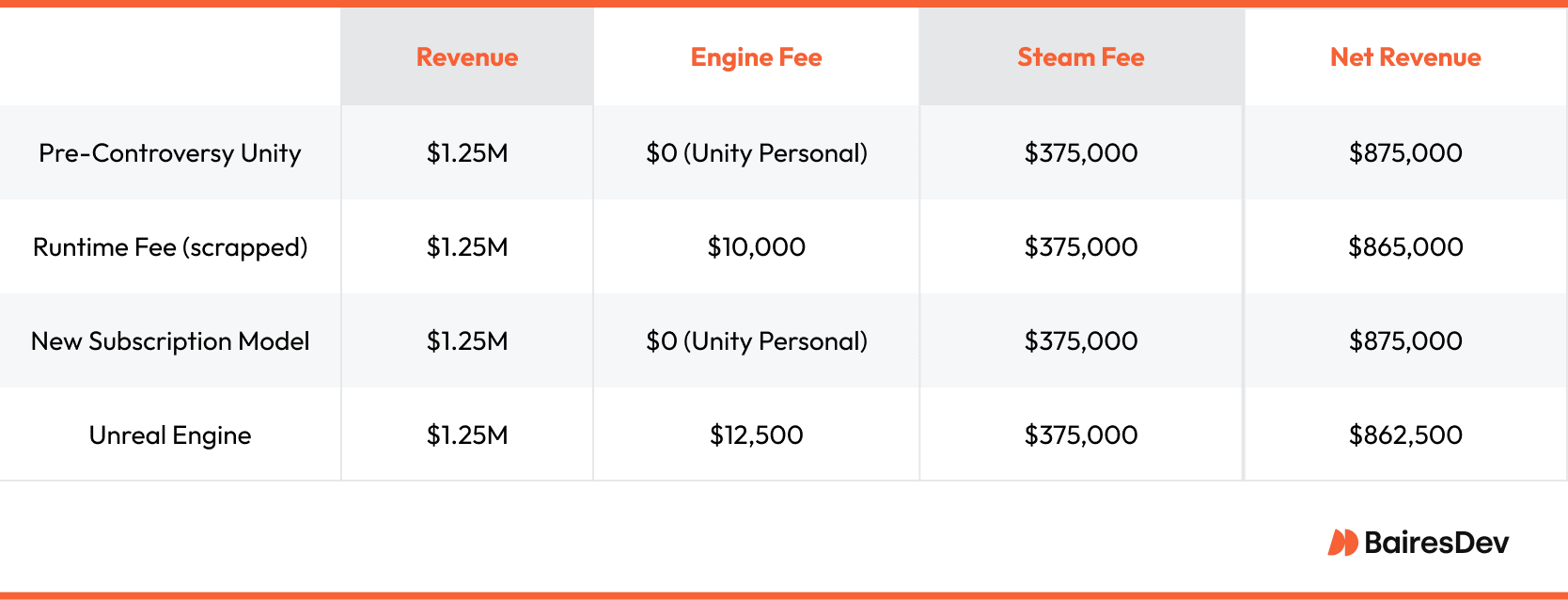
The lesson? Context matters. Not every scenario ends in disaster. Smart game developers who understood the fine print are thriving on the Unity engine. But the controversy reminds everyone that games demand careful platform decisions.
Small Games Took the Biggest Hit
The runtime fee model hurt indie developers the most. Low-cost games or free-to-play titles were particularly vulnerable. Charging per install instead of per sale sent a dangerous signal that Unity was tied to big studio profits.
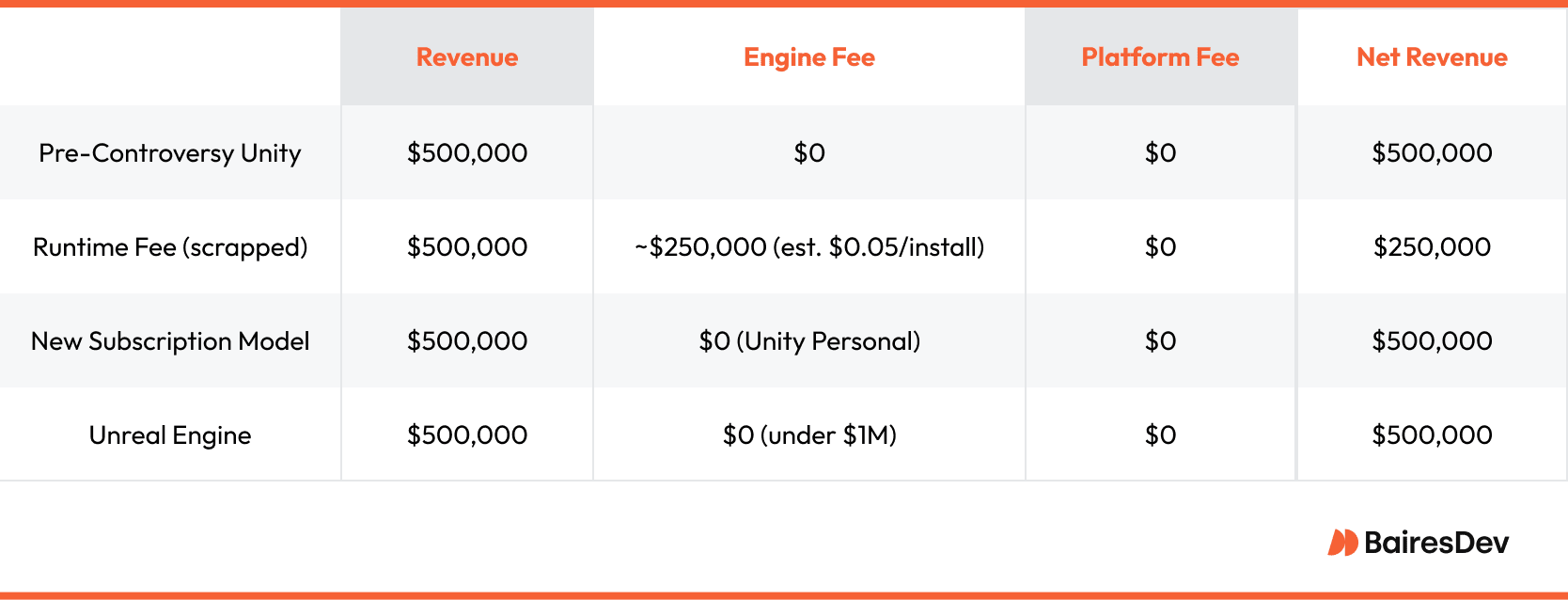
It was seen as a steep dev tax that mostly hit creators without reliable revenue models. Unity Enterprise customers were fine. Small gaming customers struggled against Scott Cawthon-sized odds.
The Install Gate Meme
Install Gate became shorthand for Unity’s blunder. The term went viral on Reddit /r/gamedev. Memes made fun of the way Unity Pro developers calculated costs using Runtime Fee Calculators. An engine exodus followed, with Godot Engine and Unreal Engine offering safe havens.
Old Model vs. New Unity Pricing: What Devs Pay Now
Unity Personal is now free for small shops under $200k current revenue. Big teams pay more. Under the new model, Unity Enterprise costs now scale based on seat count and funding ceiling. Unity Pro pricing is higher than ever, designed to offset the loss of the runtime fee. Unity Personal users avoid the direct costs. Still, the ecosystem feels divided. Engine maker trust has been eroded by what many see as tool betrayal.
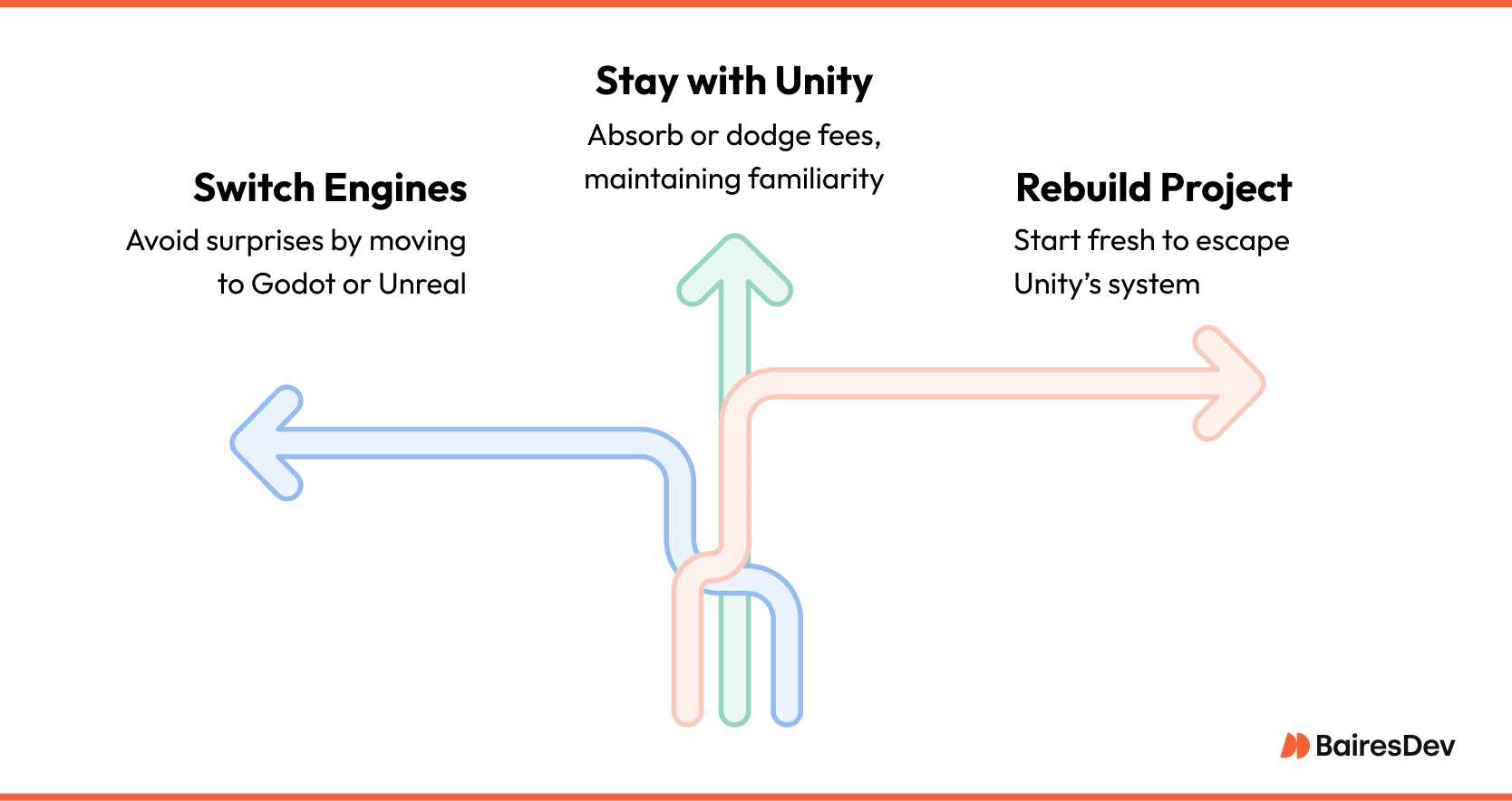
Dev Crossroads: What Unity Teams Chose After the Pricing Meltdown
When Unity announced its controversial runtime fees in 2023, developers hit a crossroads. Some stayed put. They decided the sunk costs and familiarity outweighed the new pricing. Others switched engines, citing trust issues. A few tore it all down and rebuilt from scratch.
Here’s how the dev world reacted:
- Stay: Kept using Unity Pro or Personal, absorbed or dodged new fees.
- Switch: Jumped to engines like Godot or Unreal to avoid future surprises.
- Rebuild: Started fresh to free themselves from Unity’s system, despite the risks.
Not every studio jumped ship. For many, staying was the most practical move, especially if they:
- Earned under $200K: Runtime fees didn’t apply.
- Relied on Unity workflows: Rebuilding would break budgets.
- Used Unity Personal or already budgeted for Pro: Costs were predictable.
- Worked in C#: Switching to C++ or GDScript wasn’t worth the ramp-up.
- Weren’t hit by piracy-linked installs: Install-based fees felt less risky.
Unity still offered one of the most powerful engines. For many, the fear of change outweighed the fear of fees.
What the Unity Controversy Taught Us
The Unity pricing fallout wasn’t just a money issue. It reminded developers that even tools they love can shift without warning. The smartest teams adapted. They tracked their metrics and did the math. And they made engine choices based on facts, not emotions.
Today, whether you stuck with Unity or jumped to Unreal or Godot, the lesson is: protect your margins and stay ready. In game development, the next disruption isn’t a matter of if. It’s when.






