According to Forbes, 86% of buyers will pay more for a better customer experience, yet only 1% of customers feel that vendors consistently meet their expectations. In enterprise software, that gap represents a measurable business risk, and a clear opportunity for leaders who can close it.
Usability testing is a high-leverage investment for maximizing ROI, improving customer satisfaction, and reducing release risk. It validates design assumptions early, when fixes are fastest and cheapest, and surfaces mismatches between actual and intended user behavior before they affect delivery timelines or adoption targets.
In an enterprise context, usability issues and gaps can have cascading effects:
- Missed adoption targets that jeopardize strategic programs
- Increased support volumes that drain engineering and operations bandwidth
- Customer frustration that undermines renewal rates and upsell opportunities
By integrating usability testing into every phase of the development process—from ideation and prototyping to major releases—engineering leaders can accelerate delivery, control downstream costs, and protect long-term customer value.
Key Benefits of Usability Testing for Engineering Teams
For enterprise software leaders, usability testing delivers more than just design validation — it’s a safeguard for timelines, budgets, and customer relationships. When integrated into the development process, it provides measurable business advantages that extend far beyond the product team.
- Reduced release risk. Identify usability issues before they can impact key launches, when fixes are fastest and cheapest.
- Faster delivery. Catch design flaws early, avoiding costly refactoring late in the process.
- Measurable impact. Track usability metrics like task completion rates, error frequency, and user performance alongside business KPIs.
- Higher customer satisfaction – Products that allow target users to complete tasks successfully without friction build loyalty and reduce churn.
These benefits create a compounding effect — reducing operational strain, improving adoption rates, and building the kind of consistent user experience that protects revenue and strengthens competitive position.
Usability Testing Approaches and Formats
There are several types of usability testing. The right approach depends on your business context, product complexity, target audience, and compliance landscape. Choosing correctly ensures you identify usability issues early, collect meaningful data, and align testing with your organization’s delivery goals.
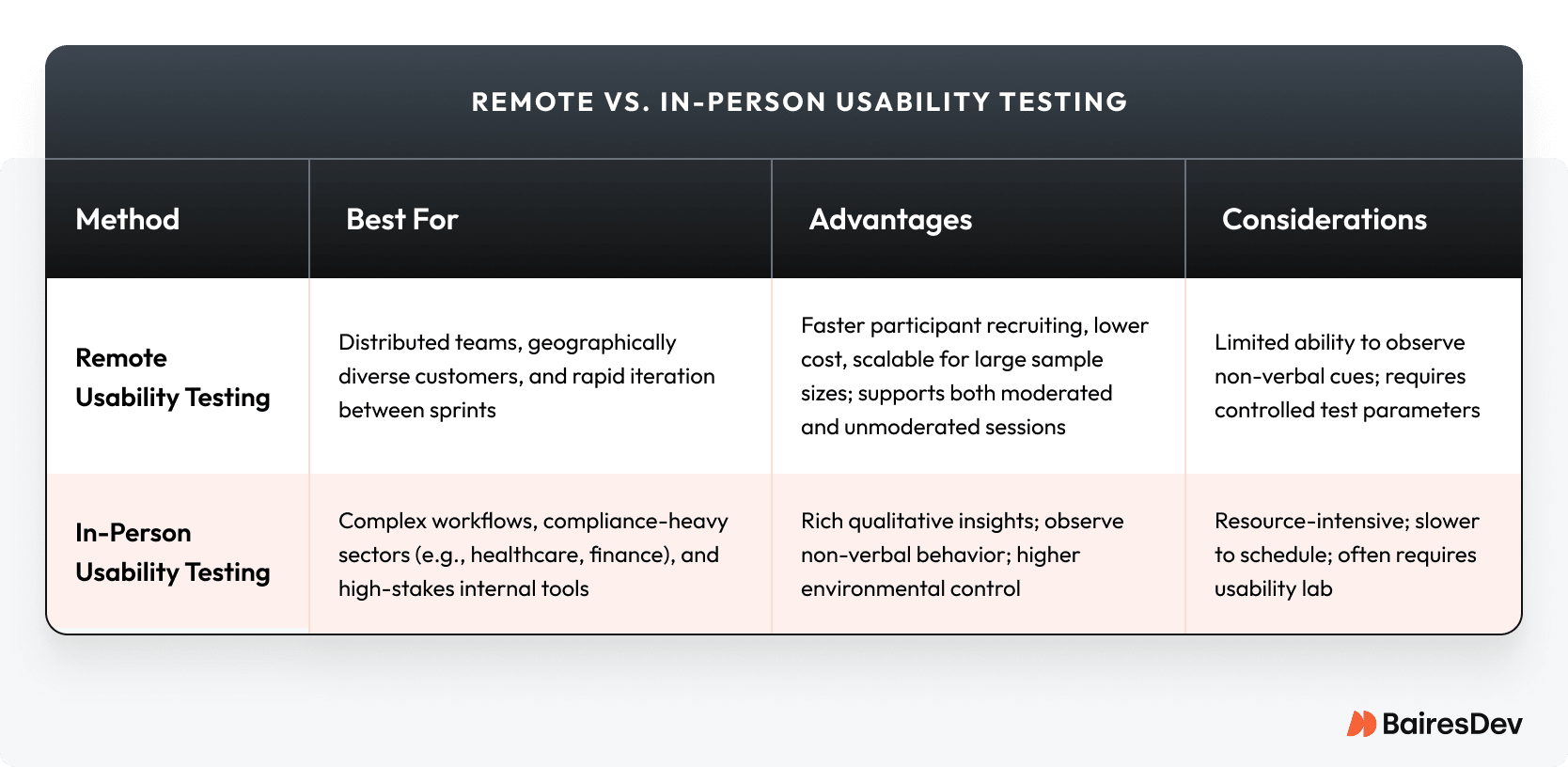
By Location and Format: Remote vs. In-Person Usability Testing
Usability testing can be conducted in different environments, each with unique advantages and trade-offs. Understanding when to use remote versus in-person usability testing ensures you collect the right information, uncover usability issues early, and match the testing method to your product’s complexity and compliance requirements.
Use this table to match test format to product complexity, compliance needs, and more.
Below we unpack what those trade-offs mean in practice for moderated and unmoderated sessions.
Remote Usability Testing
Best for distributed teams, geographically diverse target users, and rapid iteration between sprints. It allows you to gather results at scale through online tools, supports both moderated and unmoderated usability testing, and speeds participant recruiting. Considerations include limited observation of non-verbal cues and the need for controlled test parameters.
In-Person Usability Testing
Best for complex workflows, compliance-heavy sectors, and high-stakes internal tools. Provides rich qualitative insights by observing real users in a usability lab, ensuring higher environmental control. More resource-intensive, slower to schedule, and may require specialized research tools.
During remote testing, test participants complete tasks successfully using secure platforms. Moderated testing formats allow deeper probing into user behavior, while unmoderated testing delivers faster results from larger sample sizes. In-person testing sessions can satisfy compliance requirements and reveal subtle patterns — such as hesitation or undocumented workarounds — critical to overall user experience.
By Data Type: Quantitative vs. Qualitative
Quantitative usability testing focuses on success rates, time on task, and error counts to validate design changes against numeric performance over time. Commonly used in A/B testing, large-scale remote user testing, and compliance validation. This approach focuses on analyzing numerical data to understand user performance and support data-driven decision-making.
Qualitative usability testing focuses on the “why” behind usability issues through direct observation, interviews, and qualitative research. This approach considers user pain points, expectations, and needs, helping refine the user interface and workflows to improve satisfaction and adoption.
Use this quick reference when deciding what to measure and which research method will deliver the decision-making evidence you need.

With those data trade-offs in mind, these specialized testing methods map to different evidence needs and business questions.
Specialized Testing Methods
Specialized testing methods target specific business goals or user challenges and complement both qualitative and quantitative testing. Choose the method below based on whether you need quantitative evidence, qualitative context, or a mix.
- A/B testing. Ideal for validating a single change at scale, especially when tied to adoption or conversion metrics.
- Tree testing. Confirms navigation structures early, reducing redesign risk for large, content-heavy systems.
- Task analysis. Breaks down multi-step workflows to remove inefficiencies; critical for high-volume transactional systems.
- Eye-tracking studies. Track the eye movements of real users to reveal when they notice key elements and the order in which they complete workflows efficiently, improving positive user flow and aligning interfaces to intended workflows.
Implementing Usability Testing in the Development Process
Conducting usability testing effectively means aligning research methods with development milestones, compliance needs, and business objectives. A structured process ensures that both qualitative and quantitative data inform decisions at the right time—from early prototypes to post-release improvements.
Scaling Usability Testing in Enterprise Environments
Most usability tests surface the majority of issues with about five test participants per user segment. For enterprise products, segmentation by role, region, or platform ensures coverage across diverse target users. Moderated usability testing works for smaller cycles, while major releases benefit from cross-functional observation to speed consensus on design changes.
How to Conduct Usability Testing for Maximum Impact
A repeatable testing process speeds scaling: The graphic below shows the minimal, enterprise-ready loop every release should follow.
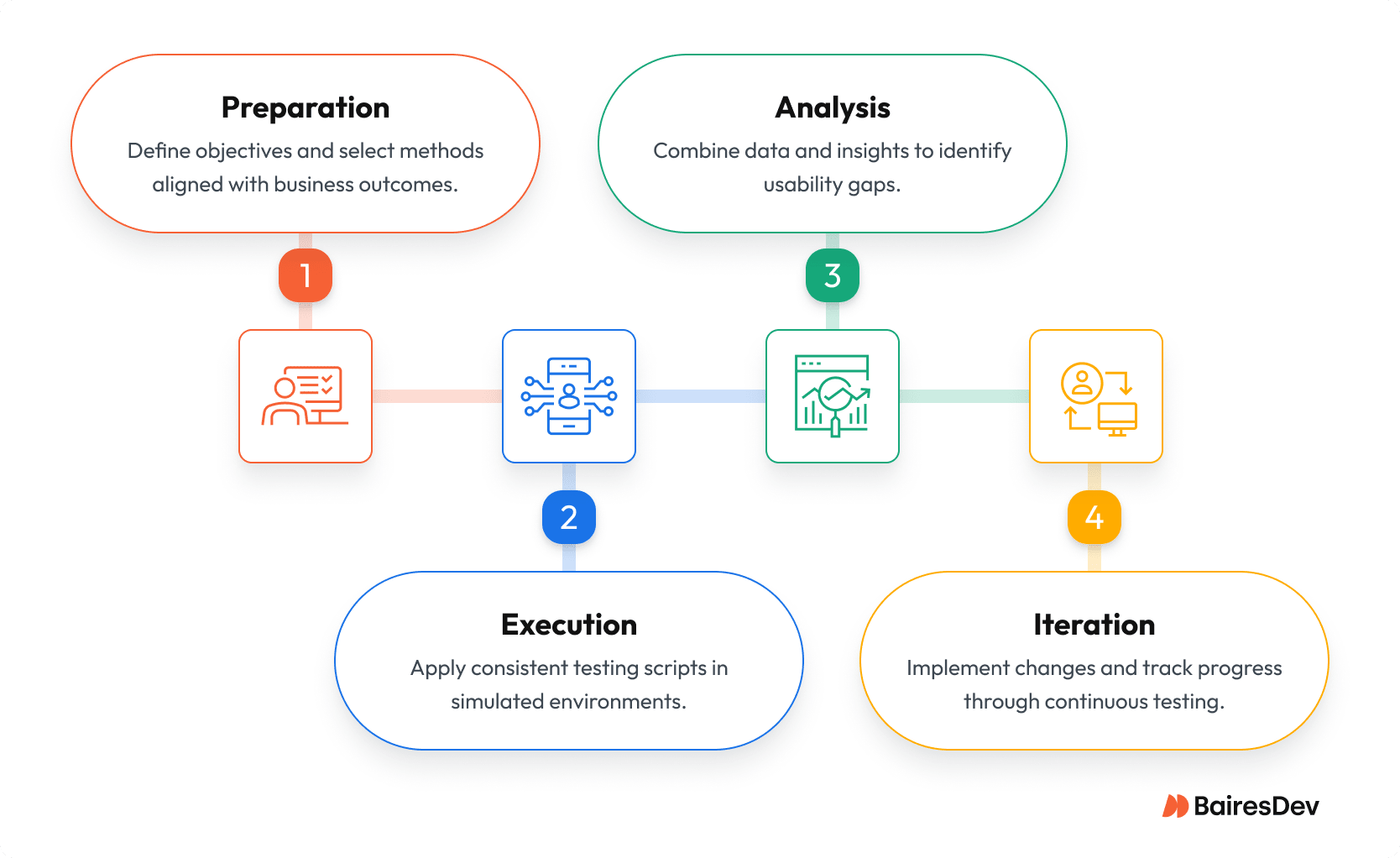
Use the process above for each segment and release; the next section explains common scaling challenges and mitigations.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Recruiting participants – Partner with recruiting vendors who specialize in your industry’s user personas to reduce screening delays.
- Stakeholder alignment – Share usability metrics and real user behavior through video clips to build consensus for design changes.
- Maintaining realistic environments – For remote testing, replicate production environments and account for device diversity.
Supporting Tools and Future Trends
Choosing the right usability testing tools and staying ahead of emerging research trends ensures enterprise teams can execute tests efficiently and adapt methods as user behaviors and technologies change.
The right combination of platforms and practices can accelerate delivery, safeguard data, and support long-term product success.
Enterprise-Grade Tools That Speed Delivery
- Screen recording and session replay tools to analyze user interactions without disrupting workflows
- Heatmaps to visualize click and scroll patterns in high-value screens
- Remote usability platforms that meet enterprise security standards and support both self-guided and unmoderated testing
- Integrated survey tools to collect both quantitative and qualitative data
- A/B testing platforms with statistical rigor for large-scale decision-making
Future-proofing Your Usability Strategy
As user expectations evolve and technology shifts, usability testing methods must adapt. Incorporating emerging research tools and techniques helps enterprise teams maintain strong user experience, stay competitive, and address usability issues before they impact adoption or satisfaction.
- AI-powered usability testing – Automates analysis of user research and accelerates feedback cycles.
- Mobile-first usability testing – Critical as mobile workflows dominate user interactions.
- VR/AR usability testing – Emerging in enterprise training and simulation environments.
- Biometric and emotion analysis – By tracking user feedback including stress, engagement, and confidence during tasks.
It’s About Your Credibility, Not Just the Code
Let’s call usability testing what it really is: a discipline for waste reduction.
Every hour an engineer spends building a feature that users can’t figure out is an hour you burned for nothing. Integrating this kind of rapid testing isn’t an “investment” in some abstract concept like “quality”; it’s a critical part of a functional delivery pipeline. It’s the most effective way to kill bad ideas before they become code and to end circular debates about design choices with cold, hard evidence of what actually works for real users.
Ultimately, this isn’t about the product as it is about your credibility. When you eliminate the noise of rework and failed features, your team’s delivery becomes predictable. Predictability earns you trust with the rest of the business. You stop being a reactive “feature factory” and start leading a team that consistently delivers measurable value. You build better software, and build a more effective and reliable engineering culture.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should we actually test?
Continuously. But here’s the simple rhythm: you test next sprint’s prototypes during this sprint. That way, feedback arrives before a single line of code is written. It prevents rework, period.
What’s the best method for a distributed team?
Remote and unmoderated. It’s fast, cheap, and gets you 80% of the way there. Only use live, moderated sessions when the workflow is brand new or mission-critical, and you absolutely need to hear the user’s tone of voice when they get stuck.
How do we measure success?
By tracking business metrics, not testing metrics. The only numbers that matter are a drop in “how-to” support tickets, an increase in adoption for new features, and a reduction in unplanned work for your engineers. If those numbers aren’t moving, you’re not succeeding.
How does this scale for multiple user types?
You don’t test every feature with every user. Focus your effort on the core workflows for your primary user persona. For secondary segments, test their critical tasks once a quarter. This is about mitigating your biggest risks, not achieving perfect coverage.
How does this fit into a sprint without slowing it down?
It happens in parallel. While engineers are building this sprint’s features, you’re testing prototypes for the next sprint. It doesn’t slow down delivery; it prevents the future rework that actually kills your velocity.
What’s the real ROI timeline?
You should find major, actionable problems within 48 hours of launching your first test. You’ll see a measurable drop in support tickets and “quick fix” requests after the very next release that includes the changes.






