In the past, business deals often took place behind closed doors. Picture a private office, a secure physical room with locked cabinets, where confidential documents were stacked neatly in folders. Only authorized people—usually one buyer or investor at a time—were allowed to enter, review the materials, and ask questions. This was the classic data room: a secure environment for handling sensitive business information.
But the way we work has changed. Today, most companies handle their high-stakes processes, from mergers and acquisitions to fundraising and legal transactions, through virtual data rooms (VDRs). These secure online platforms allow businesses to share confidential documents, manage access, and track activity, no matter where their stakeholders are located.
The Data Room industry has seen steady growth in the last decade, and it is forecasted to become a $1507 million industry by 2026, which means a solid 15% annual growth.
In this article, we’ll explore what a data room is, how it works, why it matters, and when your company might need one. We’ll also cover the key features, benefits, use cases, and decision points you need to consider.
What is a Data Room?
A data room is a controlled space, either physical or digital, where companies store, organize, and manage sensitive information. These spaces are specifically designed to allow selected people to access various documents without compromising security or confidentiality.
Think of it as the difference between handing someone a box of papers and inviting them into a monitored, locked room with rules, logs, and safeguards. With a good data room, you maintain visibility over who can see what, how long they have access, and what they’re doing inside.
The primary goal of a data room is to facilitate the due diligence process, the structured review of a company’s financials, legal status, operations, and other critical details during major transactions. Without a data room, companies risk exposing sensitive data or creating delays that can jeopardize deals.
Physical Data Rooms
Before the rise of digital tools, companies relied on physical data rooms: secure, on-site spaces where buyers, investors, or legal teams could visit and examine physical documents like contracts, financial statements, and intellectual property records.
These physical rooms were often located at the seller’s or vendor’s offices and featured tight access controls:
- Locked doors
- Surveillance cameras
- Security personnel
- Sign-in logs
- Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) for anyone entering
Only one group was usually allowed in at a time to avoid conflicts or the risk of competitive leaks.
The cost and risk associated with these setups were considerable. For multinational deals, companies had to fly in teams from various regions, coordinate schedules, and ensure documents stayed safe on-site. These limitations made physical data rooms expensive, inflexible, and difficult to scale.
Virtual Data Rooms: The Modern Alternative
Enter the virtual data room. Instead of requiring people to gather in one location, companies now use digital platforms to store and share confidential documents.
A virtual data room provides many advantages over a traditional data room:
- Remote access from anywhere in the world
- 24/7 availability
- Advanced data security measures (encryption, access controls, watermarking)
- Lower costs (no physical infrastructure or travel)
- Faster setup and easier updates when adding new documents
For example, a startup preparing for the fundraising process might set up a data room for investors to house key materials like the pitch deck, financial model, balance sheet, cap table, and legal filings. Authorized potential investors can log in, review the details, and carry out due diligence — all without waiting for physical appointments.
Similarly, large enterprises navigating liquidity events or initial public offerings (IPOs) can use a virtual data room to share complex materials with underwriters, auditors, and regulatory bodies, ensuring compliance and transparency throughout.
What are the Key Features of a Good Data Room?
Not all data rooms are created equal. A good data room combines robust security with user-friendly functionality, allowing businesses to keep information organized and accessible without sacrificing control.

Here are the key features you should look for:
- Secure access permissions: Only approved users can enter, with fine-grained control over who can view, download, or edit each document.
- Encryption: Strong encryption protocols protect data in transit and at rest, ensuring that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable to outsiders.
- Digital watermarking: Embed invisible or visible identifiers in files, allowing you to trace leaks back to the source.
- Two-factor authentication: Strengthen access control by requiring an extra verification step beyond a username and password.
- Audit trails: Detailed logs record every action, showing which authorized parties accessed which files, when, and for how long.
- Version control: Changes to documents are tracked and recorded, ensuring that all versions are accessible. This helps in maintaining a clear history of document revisions and updates.
- Indexing and search: The ability to organize various documents in a way that makes key materials easy to locate and cross-reference.
These features not only protect your confidential information but also streamline the due diligence and review process, reducing delays and minimizing time-consuming manual work.
Common Use Cases for Data Rooms
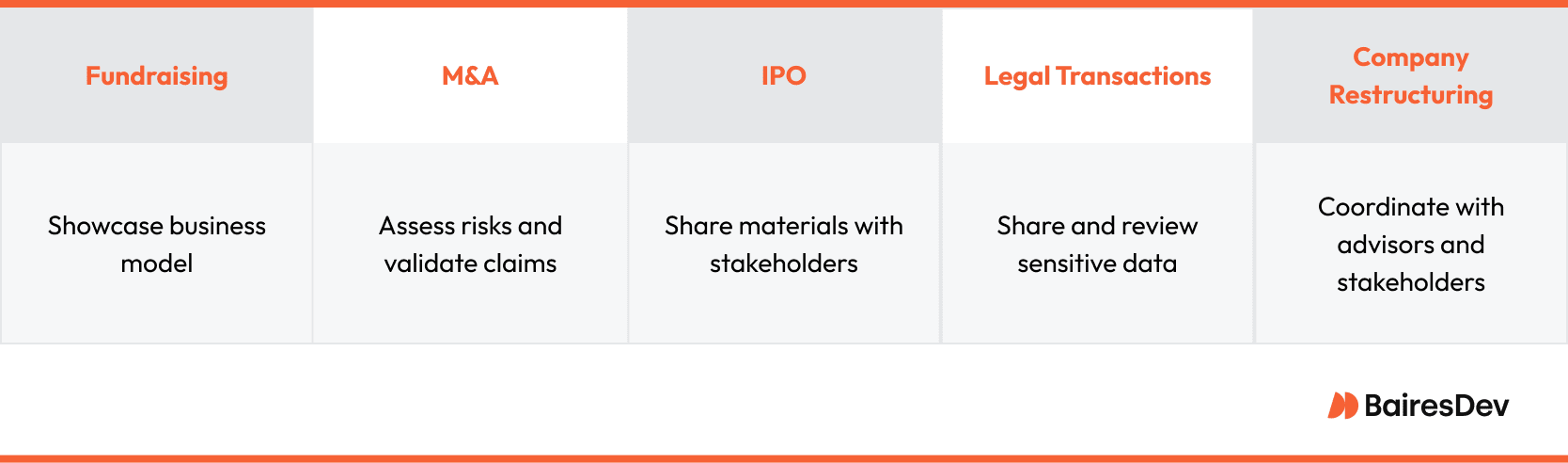
Companies use data rooms in a wide variety of situations, including:
- Fundraising: During a funding round, startups and growth-stage companies use organized data rooms to showcase their business model, financial performance, and strategic plans, giving potential investors a clear, structured view of the opportunity.
- Mergers and acquisitions (M&A): Buyers need access to detailed company records to assess risks, validate claims, and negotiate terms. A virtual data room enables this review securely and efficiently.
- Initial public offerings (IPOs): Companies preparing to go public must share sensitive materials with investment banks, underwriters, and regulatory agencies. A secure place to manage this information is essential.
- Legal transactions: Whether negotiating contracts or managing intellectual property, legal teams rely on data rooms to share and review sensitive data while maintaining confidentiality.
- Company restructuring: When reorganizing ownership or operations, companies use data rooms to coordinate with advisors, legal counsel, and stakeholders.
Beyond these formal transactions, many businesses use data rooms to manage confidential information in-house, such as R&D files or sensitive project materials across distributed teams.
Data Security and Compliance
Security is non-negotiable when it comes to data rooms. Businesses must ensure that their chosen platform meets industry standards and complies with relevant regulations, such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for companies handling EU personal data
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare-related information
- SOC 2 for cloud service providers
This means the data room should offer:
- End-to-end encryption
- Access restrictions (such as IP and geo-fencing)
- Comprehensive audit logs
- Regular security updates and compliance certifications
Without these safeguards, the risk of data breaches, leaks, or regulatory penalties rises sharply — a cost few companies can afford.
Intellectual Property Protection
Your company’s intellectual property (IP), including patents, trademarks, and proprietary data, is among its most valuable assets. Protecting it inside a data room means using advanced controls like:
- Watermarks on sensitive files
- View-only restrictions
- Disabling copy/paste or screenshot capabilities
- Tracking file access with unique identifiers
By securing IP properly, you reduce the risk of theft, misuse, or unauthorized sharing, giving your company and its investors greater peace of mind.
Google Drive vs. a Dedicated Data Room
At first glance, it might seem tempting to use Google Drive or Dropbox instead of a dedicated data room. After all, they’re familiar, affordable, and widely used. But when you’re dealing with high-stakes transactions or sensitive materials, the limitations quickly show.
Unlike standard file sharing tools, dedicated data rooms offer:
- Advanced access permissions and controls
- Higher-grade encryption and compliance measures
- Detailed audit trails and activity tracking
- Integrated tools for managing due diligence and organizing materials for review
In short, if you’re running a competitive analysis or preparing for a major deal, a dedicated virtual data room gives you the professional, secure infrastructure you need to operate with confidence.
Building Your Own Data Room
Some companies explore building their own data room in-house, especially if they operate in specialized sectors or want complete control over their systems.
The advantages include:
- Full customization to match your unique business model
- No third-party providers with potential access to your files
- Opportunities to develop proprietary solutions that could even be sold to competitors
However, the drawbacks are significant:
- High development and maintenance costs
- Long lead times to ensure robust data security and compliance
- The need for a highly skilled, dedicated technical team
- Ongoing responsibility for updates, patches, and regulatory changes
For most businesses, partnering with an established virtual data room provider offers a safer, more scalable, and cost-effective solution.
Final Takeaways
A data room plays a critical role in modern business. It allows companies to protect confidential documents, manage sensitive transactions, and operate efficiently during complex, high-stakes processes.
By investing in a good data room, you ensure your due diligence process runs smoothly, your information stays safe, and your investors and partners have the confidence they need to move forward.
In a world where data leaks or mishandled documents can derail major deals, a secure, well-structured effective data room isn’t just a convenience — it’s a business necessity.






