Data-driven decision making (DDDM) uses facts, metrics, and analysis to guide strategic business decisions. Instead of relying on intuition, leaders can transform raw data into actionable insights that align with business objectives, reduce risk, and accelerate growth.
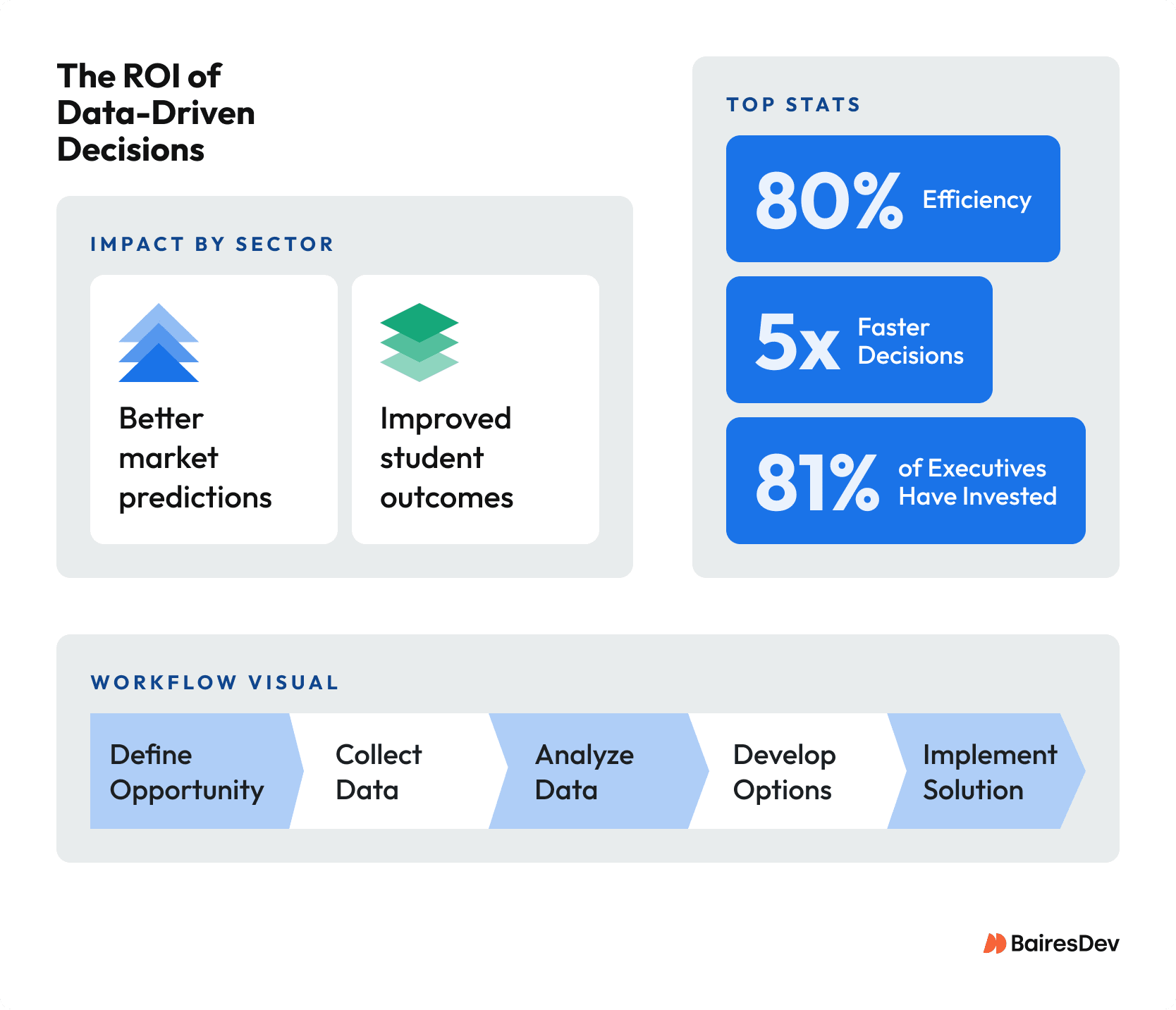
Engineering and product leaders can’t afford to rely on gut feel alone. DDDM improves operational efficiency, helps teams deliver against roadmaps, and ensures that decisions are grounded in trustworthy data rather than assumptions. Per the Harvard Business Review, while 81% of executives believe data should be at the heart of business decisions, they admit to arriving at mixed results when striving to improve data quality.
This guide explores what data-driven decision making is, how enterprises can implement it effectively, and how to avoid the pitfalls that derail most initiatives.
Understanding Data-Driven Decision Making
At its core, DDDM is the process of guiding business decisions using relevant, accurate data. It combines:
- Data analytics — quantitative analysis, statistical analysis, data visualization, and machine learning to identify patterns and trends.
- Business alignment — ensuring insights connect directly to business goals and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Cultural adoption — embedding data literacy, critical thinking, and accountability into daily workflows.
When implemented correctly, data-driven decision-making enables leaders to make informed decisions faster, with greater confidence, and with measurable impact on revenue, efficiency, and innovation.
Why It Matters
The business case for data-driven decision-making continues to strengthen:
- Companies using data analytics improve operational efficiency by up to 80%.
- Real-time analytics adoption has cut decision-making cycles from weeks to minutes in sectors like finance and healthcare.
- Organizations that integrate AI-driven analytics are five times faster at making business decisions.
For enterprise engineering leaders, this translates into faster roadmap execution, reduced delivery risk, and stronger alignment between technical capacity and business objectives.
In a landscape shaped by big data, external factors, and future trends, ignoring DDDM is no longer a neutral choice—it’s a competitive disadvantage.
The Four Key Steps in Data-Driven Decision Making
1. Define the Problem or Opportunity
Clarify the decision to be made and the business objectives it supports. Identify KPIs and data sources that will inform the decision-making process. Reliable framing at this stage helps prevent wasted effort later.
2. Collect and Analyze Data
Gather relevant data from multiple sources—customer data, operational metrics, financial data, and market trends. Use statistical analysis, predictive analytics, and reporting tools to extract actionable insights. Analyzing data effectively requires both technology and data literacy.
3. Develop and Evaluate Options
Leverage insights to generate potential solutions. Evaluate each option against business goals, resource constraints, and risk factors. This is where enterprises often combine predictive analytics with scenario modeling to draw conclusions about different pathways.
4. Implement and Monitor
Deploy the chosen solution, track performance against KPIs, and adjust based on ongoing analysis. Using dashboards, visualization tools, and machine learning models, teams can monitor outcomes in real time and transform raw data into continuous improvement.
| Step | Key Actions | Tools & Techniques | ICP-Relevant Example |
| Define | Identify problem, KPIs, data needs | Stakeholder interviews, KPI mapping | Reduce feature backlog by 20% |
| Collect & Analyze | Gather and clean data | BI tools, SQL, ML models | Analyze customer feedback for UX redesign |
| Develop & Evaluate | Generate and compare solutions | Scenario modeling, cost-benefit analysis | Choose between two cloud migration paths |
| Implement & Monitor | Deploy and track | Dashboards, A/B testing | Monitor API latency post-optimization |
Building a Data-Driven Culture
Technology alone doesn’t create a data-driven organization. Sustaining one requires:
- Data literacy — ensuring leaders and teams can interpret and challenge findings.
- Accessible tools — self-service analytics so employees can perform data analysis without bottlenecks.
- Cultural reinforcement — rewarding evidence-based decision making and critical thinking.
- Executive sponsorship — clear commitment from leadership to prioritize data over instinct.
- Governance councils — cross-functional groups that guide business decisions and maintain accountability for data use.
Enterprises that fail to build culture often see projects stall, even with the best technology. By contrast, organizations that integrate assessment literacy, feedback loops, and transparent reporting tools sustain momentum and build trust in the decision making process.
Data Management and Quality
Poor data quality is the fastest way to undermine data-driven strategies. Inaccuracies in data lead to flawed analysis and misguided outcomes. Enterprises can mitigate this by:
- Establishing data governance frameworks that ensure accuracy, compliance, and relevance.
- Enforcing data security protocols to safeguard sensitive information such as patient and financial data.
- Running regular audits to identify and correct inaccurate data.
Enterprises must also address unstructured data, multiple data sources, and the challenge of integrating external factors like shifting market trends. Without reliable data, even the most sophisticated analytics tools will generate poor outcomes.
Tools and Technologies
A modern enterprise-ready DDDM stack typically includes:
- Business intelligence platforms (Power BI, Tableau) for data visualization.
- Predictive analytics to forecast future trends and customer behavior.
- Machine learning models to detect patterns in unstructured data and automate repetitive analysis.
- Integration layers that unify raw data from multiple data sources into a single, trustworthy system of record.
Sector-Specific Applications
Business
- Optimize resource allocation based on historical data and key performance indicators.
- Build targeted marketing campaigns by analyzing customer behavior, customer feedback, and financial data.
- Use predictive analytics to anticipate market trends and guide strategic business decisions.
Education
- Leverage assessment data to inform classroom instruction and adapt teaching methods.
- Track student performance and assessment literacy to transform raw data into actionable insights for program design.
- Provide classroom teachers with reporting tools to visualize data and adjust instruction.
Healthcare
- Analyze patient data to improve treatment outcomes and reduce errors.
- Monitor KPIs to improve efficiency in hospital operations.
- Use predictive analytics and machine learning to forecast future trends in patient care and resource demand.
By tailoring approaches to sector needs, enterprises can extract actionable insights from both structured and unstructured data, turning analytics into measurable business outcomes.
The ROI of Data-Driven Decisions
Overcoming Common Barriers
- Overemphasis on tools — Culture, literacy, and governance matter as much as technology.
- Data silos — Break down silos to ensure relevant data from multiple data sources is accessible enterprise-wide.
- Slow adoption — Start with high-impact, low-risk projects to demonstrate value and build momentum.
- Poor data quality — Inaccurate data erodes trust and leads to misinformed decisions.
Data Security and Compliance
With GDPR, HIPAA, and similar regulations, data security is non-negotiable. Enterprises must:
- Encrypt sensitive data.
- Enforce strict access controls.
- Train employees to handle patient and customer data responsibly.
Protecting data effectively safeguards reputation and ensures compliance, while also enabling leaders to gather data with confidence.
A Smarter Path Forward
Data-driven decision making isn’t just a methodology—it’s a strategic advantage. For enterprise engineering leaders, it means:
- Faster delivery
- Reduced risk
- Better alignment between technical execution and business strategy
Organizations that master data-driven decision making will be the ones that adapt quickest to market changes, customer needs, and external factors. Building a data-driven culture supported by strong governance, trustworthy data, and advanced analytics tools will separate the leaders from the laggards.






