Python powers some of the world’s most critical systems, from NASA’s space missions to Netflix’s recommendation engines. It’s now the most popular programming language in the TIOBE Index (Sept 2025), and over half of developers use it, according to Stack Overflow.
For businesses evaluating technology choices, Python continues to stand out for its versatility, speed of development, and mature ecosystem. For technology leaders, that translates into faster time-to-market, easier hiring, and a stable ecosystem for analytics, automation, and AI.
Easy to Read, Easy to Write
Python’s readable syntax makes writing code simple. Developers can quickly build and maintain programs without the clutter found in other programming languages like Java, R, or C++. In practice, that means faster development, fewer defects, and simpler updates as systems evolve.
Python code looks like plain English. That’s why it has become a top choice for software developers and businesses that value efficiency.
If you’ve contracted your project to a Python outsourcing company, the language’s simplicity and ecosystem typically translate into shorter ramp-up and faster delivery than many alternatives.
A General-Purpose Powerhouse
Python is a powerful programming language used across industries and domains, including:
- Web applications with frameworks like Django and Flask
- Data analysis work and visualization
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Workflow automation
- Enterprise applications, APIs, and chatbots
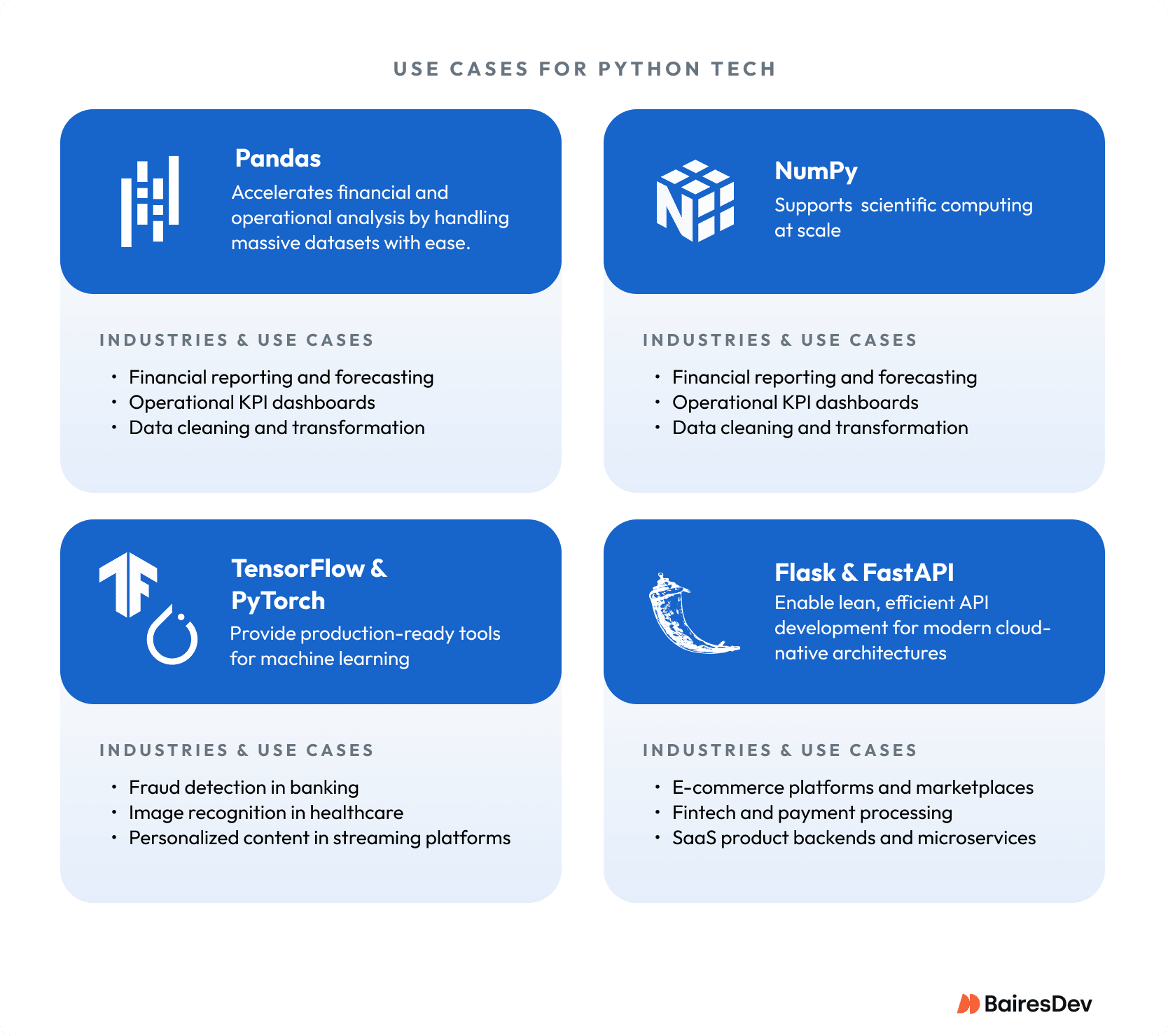
Machine learning Python libraries such as scikit-learn and TensorFlow let Python developers build advanced models for deep learning, natural language translation, and other machine learning tasks.
Real-World Applications
Python’s role in data science has grown rapidly because it simplifies working with large datasets.
Python used in data science has exploded because it simplifies working with large datasets. Libraries like pandas and NumPy make data-related tasks faster. Matplotlib and Dash add intuitive data visualization.
Learning Python
Learning Python is simple, thanks to its readable code and vast resources. This shallow learning curve means beginners and non-technical professionals can grasp the basics quickly and start their programming journey.
Experienced developers then advance to machine learning concepts, data engineering, or even web development.
For newcomers, writing code feels natural. For pros, mastering Python opens doors to building powerful machine learning models, automating workflows, or handling more complex tasks like object detection.
Cross-Platform and Compatible
Python runs on all operating systems: Windows, macOS, and Linux. With the Python interpreter, the same code works across platforms without recompiling. That cross-platform advantage saves developers time and makes software development smoother.
Compared to many other languages, Python’s portability and simple setup reduce friction when deploying across environments or consolidating tools for web, data, and ML work.
Object-Oriented and Scalable
Python is an object-oriented programming language. Developers build reusable objects, simplify debugging, and write modular applications. Data structures like lists, dictionaries, and sets make writing programs efficient while keeping the code readable.
Other programming languages often require more boilerplate. Python’s syntax reduces complexity, which is why Python remains central to machine learning projects.
Debugging and Software Testing
Python’s frameworks make software testing straightforward. Tools for unit testing and automation catch errors early, helping software developers maintain clean, reliable code.
Readable syntax plus strong testing and debugging tools means teams can iterate quickly and maintain more reliable code over time.
Advanced Topics
One of Python’s biggest strengths is its ecosystem. In practice, that means teams can assemble solutions from mature, well-maintained libraries instead of reinventing core components. Common enterprise use cases include:
- Deep learning with TensorFlow and Keras
- Natural language applications, including translation and speech recognition
- Machine learning models for regression, classification, and clustering
- Task automation for complex workflows
- Web development python frameworks for scalable apps
Python offers libraries for every challenge—data engineering, computer vision, or analyzing big data.
The Power of the Ecosystem
One of Python’s biggest strengths is its ecosystem. In practice, this means you don’t need to reinvent the wheel.
How Python Can Speed Up Delivery and Scale in Your Projects
Python’s simple syntax and large library ecosystem help teams build and test quickly. It handles data-heavy tasks, automation, and cross-platform systems well—making it a solid choice for scaling real-world applications.
Python’s versatility, readable code, and massive ecosystem are why it remains a default choice for new products, data platforms, and automation across industries.
Trade-Offs and Risks: What Decision-Makers Should Know
While Python offers clear advantages, business leaders should also weigh its trade-offs. Compared to other languages like Java or C++, Python code can run slower and consume more memory.
For machine learning tasks or data science experiments, this may not be critical. But for performance-intensive systems—such as high-frequency trading platforms—other languages may still be preferred.
Another challenge at scale is consistency: with large teams of Python developers, enforcing readable code, managing dependencies, and ensuring software testing standards are essential.
As a business, you need to establish strong practices in software development, version control, and code review to mitigate these risks. Understanding these trade-offs will help you make informed choices about when and where Python is best used.
Why Outsourcing Python Projects to an Experienced Partner Will Make a Difference
Outsourcing Python development to a skilled partner can significantly reduce risk and accelerate delivery. An experienced team brings proven frameworks, industry best practices, and expertise in Python’s ecosystem—from machine learning Python libraries to web development Python frameworks.
For enterprises without in-house specialists, this ensures access to advanced Python skills in areas like data engineering, deep learning, and natural language processing.
Outsourcing also helps organizations scale resources flexibly: adding Python developers for a product launch, or engaging machine learning engineers for targeted machine learning concepts and data-related tasks.





