CRM implementation is more than rolling out software. For most organizations, it’s a business transformation that reshapes customer relationships, sales processes, and internal workflows.
A successful implementation can increase customer retention, improve sales team efficiency, and provide deeper business intelligence. But many companies underestimate the complexity of the CRM implementation process.
From data migration to aligning stakeholders and integrating legacy systems, each step carries risks. Missteps often lead to stalled adoption, wasted investments, and frustrated sales representatives. This article breaks down the five biggest obstacles companies face and provides practical strategies to ensure your customer relationship management journey delivers measurable results.
Minimal Management Buy-In
Every CRM implementation project needs champions—and the higher up, the better. Without strong executive support, even the best CRM system can fail to gain traction across the organization.
Why Support May Be Lacking
- Leadership may view CRM software as a tactical tool, not a strategic platform.
- Mid-level managers may not be sure how the implementation strategy supports their goals.
- Sales representatives and other end users don’t see how the system improves daily workflows.
The Business Impact
Without buy-in, CRM quality and effectiveness stalls. Sales teams revert to spreadsheets, customer data remains fragmented, and investments in CRM solutions never achieve expected ROI. Worse, resistance to change can spread across departments, damaging user and team adoption rates.
How to Fix It
- Secure C-suite sponsorship early. Executives should communicate the “why” of the implementation process, not just the “what.”
- Involve influential employees. Pilot programs with trusted managers and sales representatives build credibility.
- Share proof points. Demonstrating outcomes like increased customer loyalty or reduced support costs helps align stakeholders.
Recent analyst research consistently links CRM failure to weak sponsorship and change management.
For example, Forrester’s 2023 analysis shows widespread CRM adoption but persistent organizational challenges—including cooperation and change management—while consultant studies highlight that missing or inactive executive sponsors is a common, recurring cause of CRM project failure.
Panorama Consulting’s 2023 review echoes this point, identifying missing executive sponsorship, low user and team adoption, and inadequate data management as the three most common root causes of failed CRM initiatives. A committed implementation team led by senior management can avoid this pitfall.
Ill-Defined CRM Implementation Strategy
Buying a new CRM system isn’t a strategy—it’s a tool. Without a clear roadmap, organizations risk rolling out a CRM platform that doesn’t meet business needs.
Common Mistakes
- Setting vague objectives like “improve customer relationships” without measurable KPIs.
- Overlooking how the implementation plan fits into existing workflows.
- Having poor alignment between sales, marketing, and customer support teams.
The Business Impact
An unclear CRM implementation project often results in duplicated efforts, frustrated sales representatives, and missed opportunities to serve customers effectively. When CRM functionality isn’t tied to business operations, companies end up with a new system that feels like extra work instead of a productivity enabler.
What Success Looks Like
- Defined KPIs. Goals such as “increase sales calls by 25%” or “reduce missed follow-ups by 100%.”
- Clear CRM implementation strategy. A documented plan connecting features to business processes.
- Cross-team alignment. Sales, marketing, and service teams share a unified understanding of customer interactions.
A project manager or CRM consultant can help translate broad business objectives into a detailed implementation plan, ensuring every feature supports measurable outcomes. Recent industry reports suggest CRM project failure rates still range between 20% and 70%, but most problems come back to five familiar themes: leadership, adoption, data, integration, and strategy.
Causes of CRM Failure
| Root cause | Summary |
|---|---|
| Executive sponsorship / leadership | Repeatedly cited as a leading non-technical failure cause; projects without active sponsors lose momentum and budget focus. |
| User adoption / people & process | High adoption does not equal satisfaction; poor change management reduces long-term value. |
| Data quality & migration | Dirty, duplicate, or mismapped records lead to low trust and reduced CRM usage. |
| Integration / existing systems | Lack of seamless data flow with ERP/ecommerce causes silos and duplicate work. |
| Poor strategy / vague KPIs | No KPI alignment leads to feature creep, wasted customization, and unclear ROI. |
With these root causes in mind, let’s look more closely at how data migration often becomes the hidden make-or-break factor in CRM projects.
Ineffective Migration Planning
Data migration is often the most underestimated step in the implementation process—but it’s critical for long-term CRM quality and effectiveness. Poor planning creates bad data, frustrated users, and delayed go-lives.
Why the Migration of Data Matters
A CRM system is only as strong as the customer data inside it. If the migration process is rushed, companies risk losing valuable customer interactions, damaging trust with sales representatives, and weakening customer relationships.
Key Phases to Include
- Analysis: Audit existing and legacy systems and identify gaps in customer data.
- Data assessment: Flag duplicates, incomplete records, and compliance risks.
- CRM configuration: Ensure fields and workflows match specific business processes.
- Migrating data: Clean, validate, and map before transfer.
- Integration: Align CRM solutions with existing tools to ensure seamless data flow.
- User training: Train sales and other relevant teams and support staff before launch.
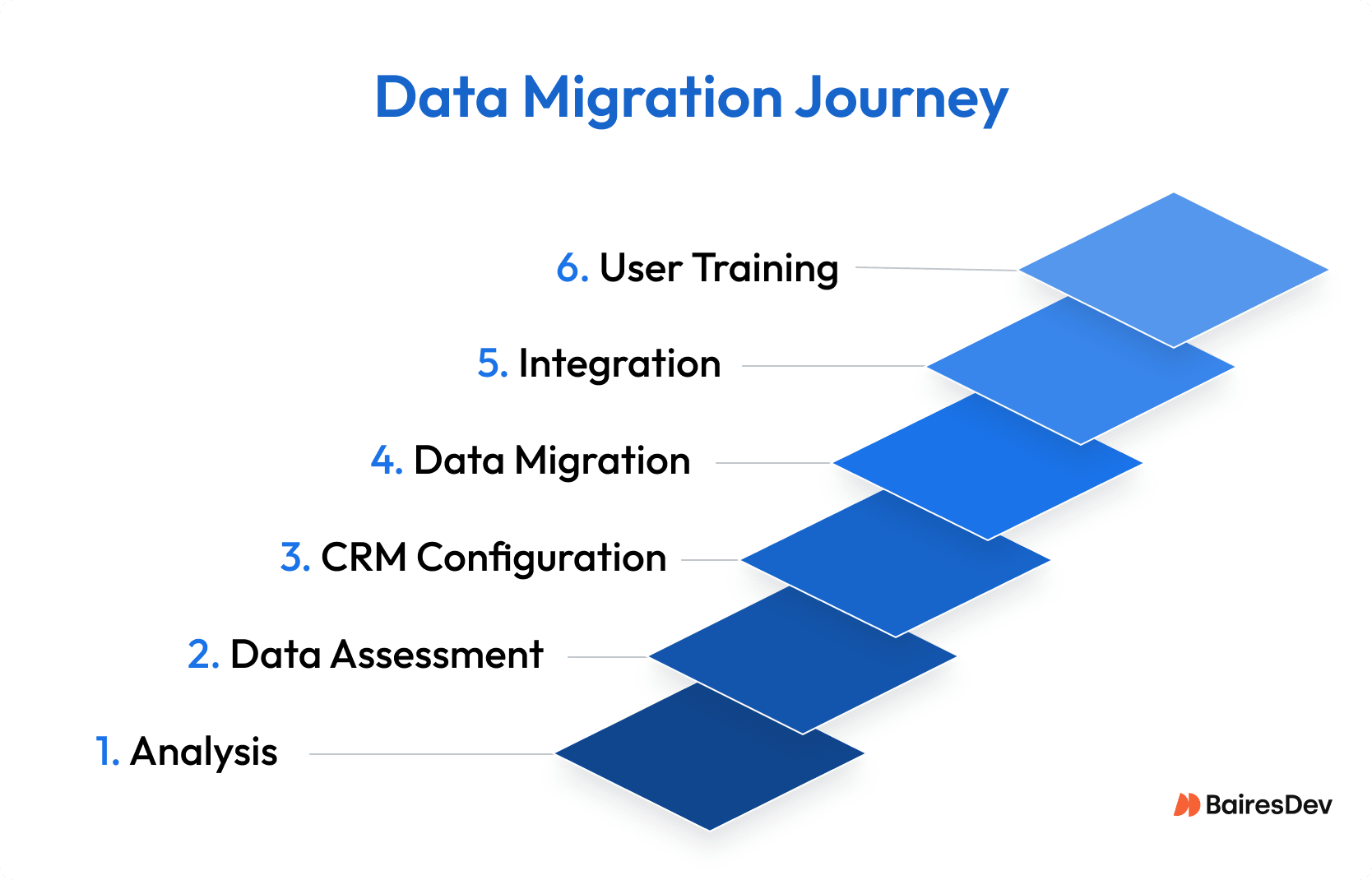
Following a structured migration process like this reduces the risk of bad data undermining the effectiveness of your CRM and helps maintain user trust.
Business Example
In 2016, Vodafone consolidated more than 28.5 million customer accounts across seven billing platforms into a unified CRM and billing system. Mapping errors during migration led to billing mistakes, disrupted service, a surge in complaints, and a £4.6 million regulatory fine.
The fallout included a noticeable drop in UK sales and reputational damage. This is a clear example of how gaps in migration planning and data mapping can turn into churn, regulatory risk, and revenue loss.
Ignoring Risks
CRM implementation isn’t risk-free. From budget overruns to poor adoption, unaddressed risks create costly setbacks.
Common Risks
- Cost overruns: Customization and workflow automation projects balloon without scope control.
- Low adoption: Sales representatives resist using new systems that don’t align with existing processes.
- Integration issues: CRMs that don’t sync with existing tools become silos.
- Support costs: Ongoing fixes drain budgets if not anticipated in the implementation plan.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct a risk assessment. Review budget, resources, and integration dependencies.
- Involve users. Including individual sales representatives in feature selection improves user and team adoption.
- Pilot programs. Test data migration and workflow automation with a small group before scaling.
- Continuous improvement. Schedule reviews to adapt the CRM system as business needs evolve.
A strong team anticipates risks and builds buffers into the implementation project. Ignoring these factors sets companies up for unnecessary disruption. Forrester’s 2023 research confirms that while CRM adoption is high across industries, satisfaction lags significantly, underscoring that risk management isn’t only about go-live. It’s about ongoing organizational alignment and sustaining satisfaction.
Choosing the Wrong CRM System
Not every CRM platform is built for every business. Selecting the wrong CRM software leads to wasted investment, frustrated users, and missed growth opportunities.
Must-Have Features
- Seamless communication. Messaging tools integrated with customer data.
- Workflow automation. Automated reminders and task routing.
- Accurate forecasting. Use business intelligence for revenue and earnings growth projections.
- Custom reporting. Track KPIs like customer retention and user adoption.
Evaluation Tips
- Prioritize CRM functionality that maps to specific business processes.
- Ensure the new CRM system integrates with existing workflows and tools.
- Engage a CRM consultant or CRM implementation partner who understands your industry.
Why It Matters
A healthcare provider selected a CRM system without checking compatibility with its existing and legacy systems. The result? Sales teams had to maintain duplicate records, creating confusion and reducing customer satisfaction. Choosing the right CRM platform upfront could have avoided months of disruption.
Beyond the Finish Line
CRM implementation doesn’t end at go-live. Continuous improvement ensures the system evolves with your business and maintains CRM quality and effectiveness over time.
- Measure CRM effectiveness. Recent 2024 benchmarks highlight three post-implementation KPIs as the most reliable indicators of effectiveness: customer retention, revenue growth, and user and team adoption.
- Monitor adoption. Train new users regularly and improve the user interface where friction exists.
- Plan for CRM customization. Adapt workflows and dashboards as operations shift.
- Maintain the CRM journey. Regular reviews with your team ensure alignment with customer needs and business intelligence goals.
When companies invest in the right implementation strategy, supported by a strong implementation team and a trusted CRM implementation partner, the platform becomes more than software—it becomes the foundation for stronger customer relationships, efficient business operations, and long-term growth.






