A sanity test is a preliminary assessment that is deployed to determine whether or not a software application or system is ready for further testing. The sanity testing process focuses on verifying the functionalities after any changes or fixes are made. Automated testing is often used to perform sanity tests, ensuring that basic functionalities are checked efficiently after each new build or release. It is crucial to verify the existing functionality to ensure that new code or changes do not disrupt current features or compromise the stability of the application.
Unlike more rigorous tests, sanity tests are superficial; they simply detect any major issues early on in the development lifecycle to help you save coveted time and resources. This way, you can make any easy fixes rather than going on to test a fundamentally flawed application or system.
What Is Sanity Testing?
Sanity testing, a subset of regression testing, acts as a cursory check. It targets key areas of an application or system, focusing on its functionalities. In short, a sanity test verifies that the functions work as intended before the application or system moves on to more exhaustive testing.
Purpose and Scope
Sometimes, when a team fixes a particular function or makes modifications to software, they might break or interfere with another function. Testing is important to make sure that any changes made to one aspect of the software don’t adversely affect another aspect of it.
If sanity testing fails, it indicates issues with specific features or functionalities, prompting the development team to troubleshoot before proceeding with extensive testing. This highlights the importance of sanity testing as a quick verification step after smoke testing, ensuring that any critical problems are addressed promptly.
You should perform sanity testing throughout the development cycle to ensure that a specific function or particular section of the software works as intended—especially after any modifications or fixes. It is essentially a quick check to make sure that all major functionalities function correctly before forging forward.
It’s important to understand that a sanity check is not about comprehensive testing; rather, it’s about confirming that the software is ready for comprehensive testing. By concentrating on specific areas within a limited testing scope, a sanity check can efficiently identify any potential issues, ensuring the overall stability and health of the software.
Key Characteristics
Sanity tests are distinguishable by a few key characteristics:
- Narrow scope
- A focus on specific functionalities or sections of the software
- Quick execution time
- Non-scripted nation (no detailed test scripts or predefined test cases)
- Basic validation that recent changes or fixes haven’t caused major issues
- Informal approach
When to Use a Sanity Test
There are various use cases for a sanity test. Here are some of the most common reasons a development team and testing team would implement a sanity test.
Post-Bug Fixes
Sanity testing is essential after a bug fix. A sanity test ensures that the bug fix hasn’t introduced any new issues and that the original problem is truly resolved.
After Regression Testing
It’s important to perform smoke and sanity testing after regression testing to confirm that any core functionalities remain unaffected and intact despite any changes made in the codebase.
Following Minor Changes
When developers make minor changes or patches to the software, sanity testing checks validate that those changes (even minor alterations) haven’t adversely affected any main functionalities.
Before Release
Before a product release or before moving to other more extensive testing phases, sanity testing can confirm the software’s stability. The features of sanity testing include a quick and targeted evaluation method used to assess specific areas of an application following recent changes. These tests prioritize critical functionalities and are less comprehensive than full regression testing, allowing for fast verification of system stability while still ensuring essential components are functioning as intended.
During Tight Deadlines
In agile environments or projects with tight deadlines, sanity testing offers a way to quickly validate critical functionalities without extensive test coverage. This is especially important for time-sensitive projects.
When Test Environment Changes
If there are any changes made in the test environment, such as an update or configuration modification, a sanity test helps to ensure that the test environments are stable for more comprehensive testing.
After Integration of Modules
After software modules or components are added, testing efforts are necessary to quickly confirm their seamless integration into the existing system. This test checks that the other features still function after the addition.
How Sanity Tests Differ from Other Types
There are many types of tests to check the functionality of a system and inspect it for any bugs. A sanity test is just one specific type of test. Here’s how it compares to other common types of testing.
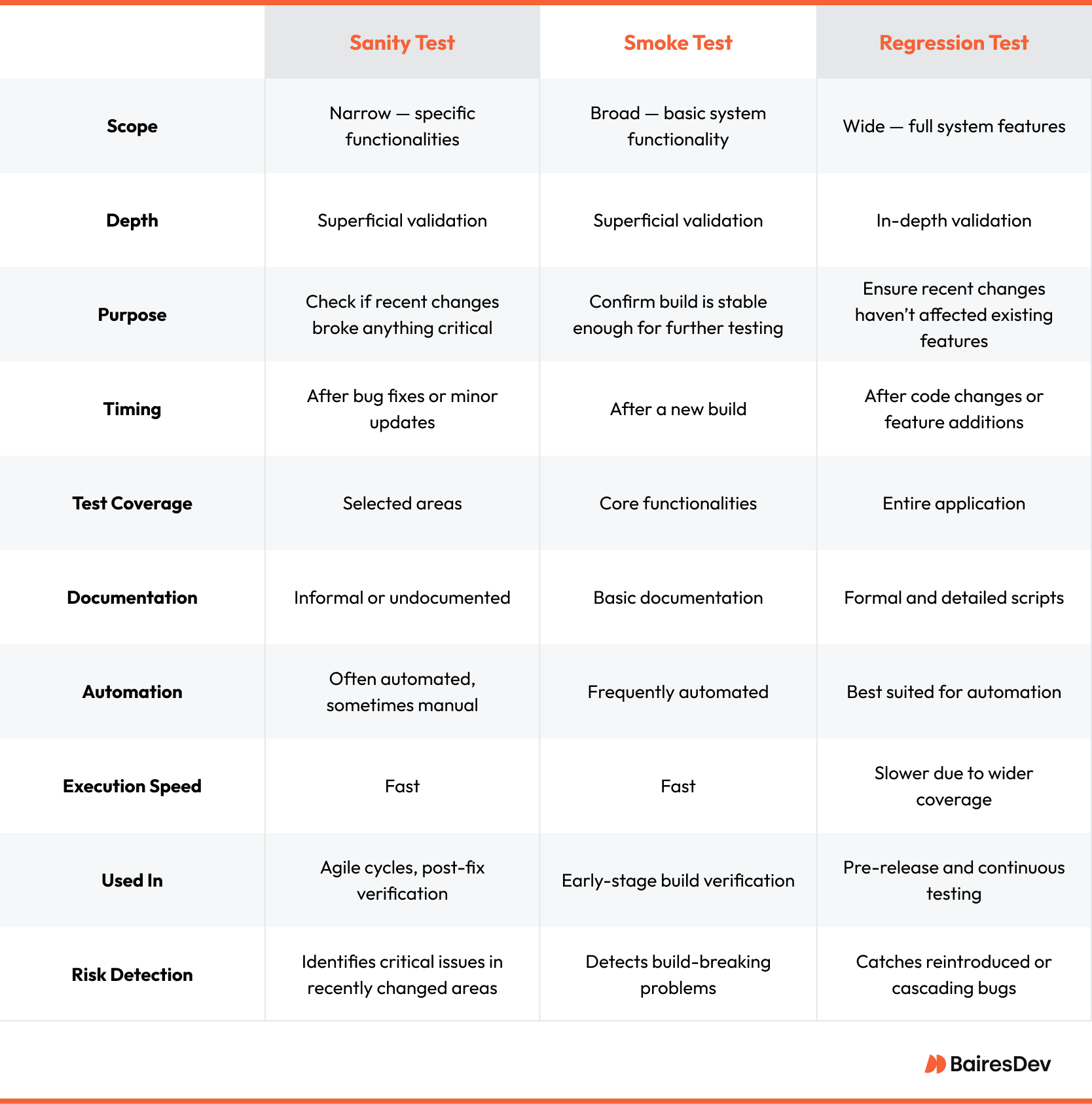
Compared to Smoke Testing
While a sanity test and a smoke test are both surface-level tests, sanity testing focuses on specific features, while smoke testing assesses the basic functionality of the entire system.
Cloud-based environments offer significant advantages for mobile app testing, facilitating both manual and automated sanity tests with tools like LambdaTest.
Compared to Regression Testing
Both sanity tests and regression tests are important after you introduce changes. Identifying critical issues during sanity testing is crucial as it enables teams to promptly address potential problems, streamline resource allocation, and maintain software quality. However, regression tests check for new bugs after changes, while sanity tests check the functionality of specific features after changes.
Manual vs Automated Sanity Testing
Sanity testing can be performed manually or through automation, each approach offering unique advantages and disadvantages.
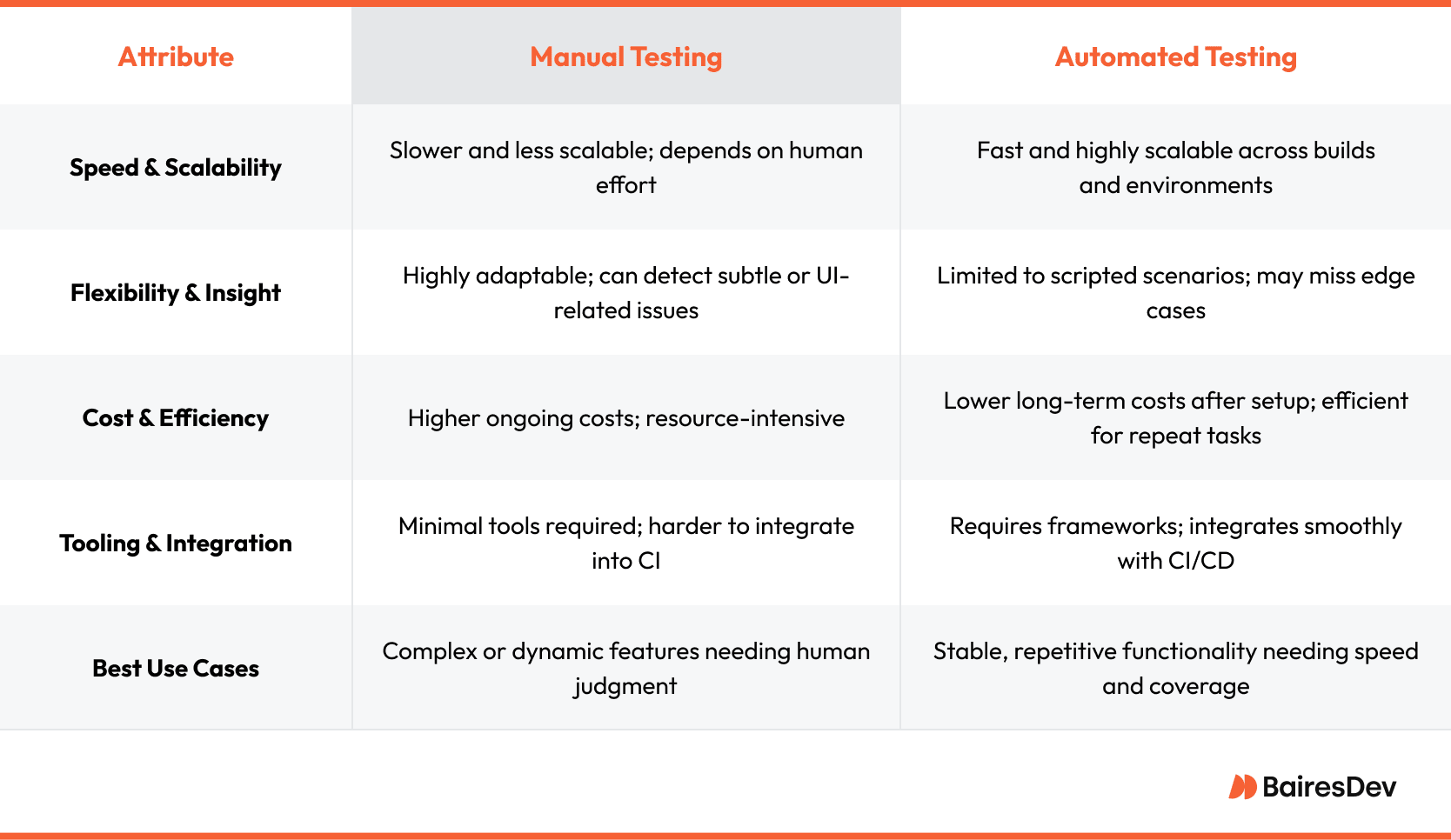
Advantages of Manual Testing
Manual sanity testing allows testers to delve deeper into the software application, exploring its functionality in a way that automated tests might miss. This hands-on approach enables testers to identify subtle issues and nuances that automated scripts may overlook. Manual testing is particularly beneficial for applications with complex or dynamic functionality, where human intuition and adaptability can play a crucial role. Additionally, manual sanity testing provides the flexibility to adjust the testing approach in real-time based on the application’s behavior, ensuring a thorough examination of the software.
Benefits of Automation
Automated sanity testing, on the other hand, brings efficiency and speed to the testing process. Automated tests can be executed repeatedly and quickly, significantly reducing the time and effort required for testing. This is especially useful for applications with repetitive or straightforward functionality, where automated scripts can cover a wide range of test cases and scenarios. Automation also enhances the overall coverage of the testing process, ensuring that no critical functionalities are missed. By integrating automated sanity tests into the continuous integration pipeline, development teams can receive rapid feedback on the stability of their software builds.
Choosing the Right Approach
The choice between manual and automated sanity testing depends on the specific needs and goals of the testing process. Manual testing is ideal for applications with intricate or evolving functionalities, where a human touch is necessary to uncover hidden issues. Automated testing, however, is more effective for applications with repetitive tasks, providing quick and consistent results. Ultimately, a combination of both manual and automated testing approaches can ensure comprehensive coverage and efficient testing, leveraging the strengths of each method to maintain software quality.
Automation Tools for Sanity Testing
Automation tools play a pivotal role in streamlining the sanity testing process, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Popular Tools
- Selenium: Selenium is an open-source tool widely used for automating web browsers. It supports multiple programming languages, such as Java, Python, and C#, and allows for flexible test scripting. Selenium is ideal for sanity testing web applications across various browsers and platforms.
- Appium: Appium is a popular tool for automating mobile applications. It supports multiple platforms, including iOS and Android, and allows testers to write tests using their preferred programming languages. Appium’s versatility makes it a valuable tool for sanity testing mobile apps.
- TestComplete: TestComplete is a commercial tool designed for automating functional and regression testing. It supports a wide range of applications, including desktop, web, and mobile. TestComplete’s robust features make it suitable for performing sanity tests, ensuring that recent changes or bug fixes function correctly.
- Ranorex: Ranorex is another commercial tool that excels in automating functional and regression testing. It offers a user-friendly interface and supports a variety of applications. Ranorex’s capabilities extend to sanity testing, providing reliable and efficient test automation.
- Cucumber: Cucumber is an open-source tool for behavior-driven development (BDD). It allows testers to write test cases in plain language, making it accessible to non-technical stakeholders. Cucumber can be used for both sanity testing and acceptance testing, bridging the gap between technical and business teams.
These automation tools can significantly enhance the sanity testing process, increasing efficiency and reducing the time and effort required for testing. By leveraging these tools, development teams can ensure that their software applications remain stable and functional, even after changes or bug fixes.
Prioritize Critical Functionalities
Several functionalities are crucial to a software’s operation. Here are some key tips for determining what makes a functionality critical and assessing the importance and impact of testing that functionality.
Keep It Unscripted
Sanity testing, also known as surface level testing, is always informal. Informal tests take up less time than more comprehensive tests, so there is room for flexibility and creativity in this approach. The unscripted nature of this type of testing is enough to uncover unexpected issues without diving too deep into the whole system.
Fast Feedback is Crucial
Rapid feedback loops are important to keep the development cycle move along. Smoke testing checks provide rapid feedback on the overall stability of the software. It’s also essential for staying aligned with your timeline and goals. A sanity test provides quick, actionable insights that can significantly accelerate development and rectification processes.
Ensure Scalability
To ensure scalability, adopt modular test design methodologies. It’s also important to select testing tools that offer scalability features. This allows sanity tests to adapt and expand with the project’s growth and evolving requirements.
Document Results Succinctly
Unlike other types of tests, sanity tests don’t necessarily result in extensive documentation. However, the concise documentation of sanity testing results can aid in faster decision-making and subsequent testing phases.
Incorporate Into Continuous Integration (CI)
Build verification testing fits into continuous integration (CI) pipelines by automating post-build sanity checks. This type of testing ensures that critical functionalities remain deployable, enhancing development efficiency and minimizing the risk of deploying faulty code to production.
Leverage Team Insights
There is value in involving the broader team, including developers, designers, and product managers, in sanity testing. Conclusion sanity testing plays a crucial role in quickly identifying issues and determining if further testing is necessary. Each team member can provide diverse insights that enhance the effectiveness of sanity tests.
Focus on User Experience
Testing from a user’s perspective helps ensure that the core user journey remains intact.
- Review user narratives and requirements to identify critical interactions
- Prioritize high-impact features over less-important ones for sanity testing
- Collaborate with all key stakeholders to define key user interactions because they may have different ideas of what’s important to users
- Conduct usability studies to pinpoint important user interactions
- Analyze user behavior data to identify frequently used features
- Include edge cases in sanity testing
Iterate and Evolve Testing Criteria
Sanity tests are intentionally flexible. They leave room for iterative review and the refinement of testing criteria based on past learnings and product evolution. Evolving testing methods is crucial to maintain the relevance of sanity tests. This level of adaptability is important for maintaining the relevance of sanity tests.
The following are some of the most widely used tools in the industry for conducting sanity tests:
- Selenium: Selenium is an open-source automation tool. It is primarily used for testing web applications. It supports multiple programming languages, such as Java, Python, and C#. It also allows for flexible test scripting and facilitates the automation of sanity tests across various browsers and platforms.
- JUnit: JUnit is a popular Java testing framework for writing and executing unit tests. It provides testers with annotations to define test methods and assertions to verify expected outcomes. It simplifies the process of writing and running sanity tests.
- TestNG: TestNG is a testing framework inspired by JUnit and NUnit. Its functionalities for testing include parameterization, grouping, and parallel execution. It supports various annotations and assertions for defining and validating test cases.
- Robot Framework: Robot Framework is an open-source test automation framework driven by keywords. It supports various test libraries and platforms and offers a simple, readable syntax for writing test cases. It also has built-in support for web, API, and mobile testing.
- Postman: Postman is a user-friendly API testing tool. It allows testers to create and execute API requests, automate workflows, and perform regression and sanity tests on APIs. Environment variables, collections, and assertions are just a few of the features that streamline testing processes.
Benefits of Sanity Test
There are plenty of pros to sanity tests, which is why they are so common throughout the development lifecycle. Here are a few of the key benefits of sanity tests.
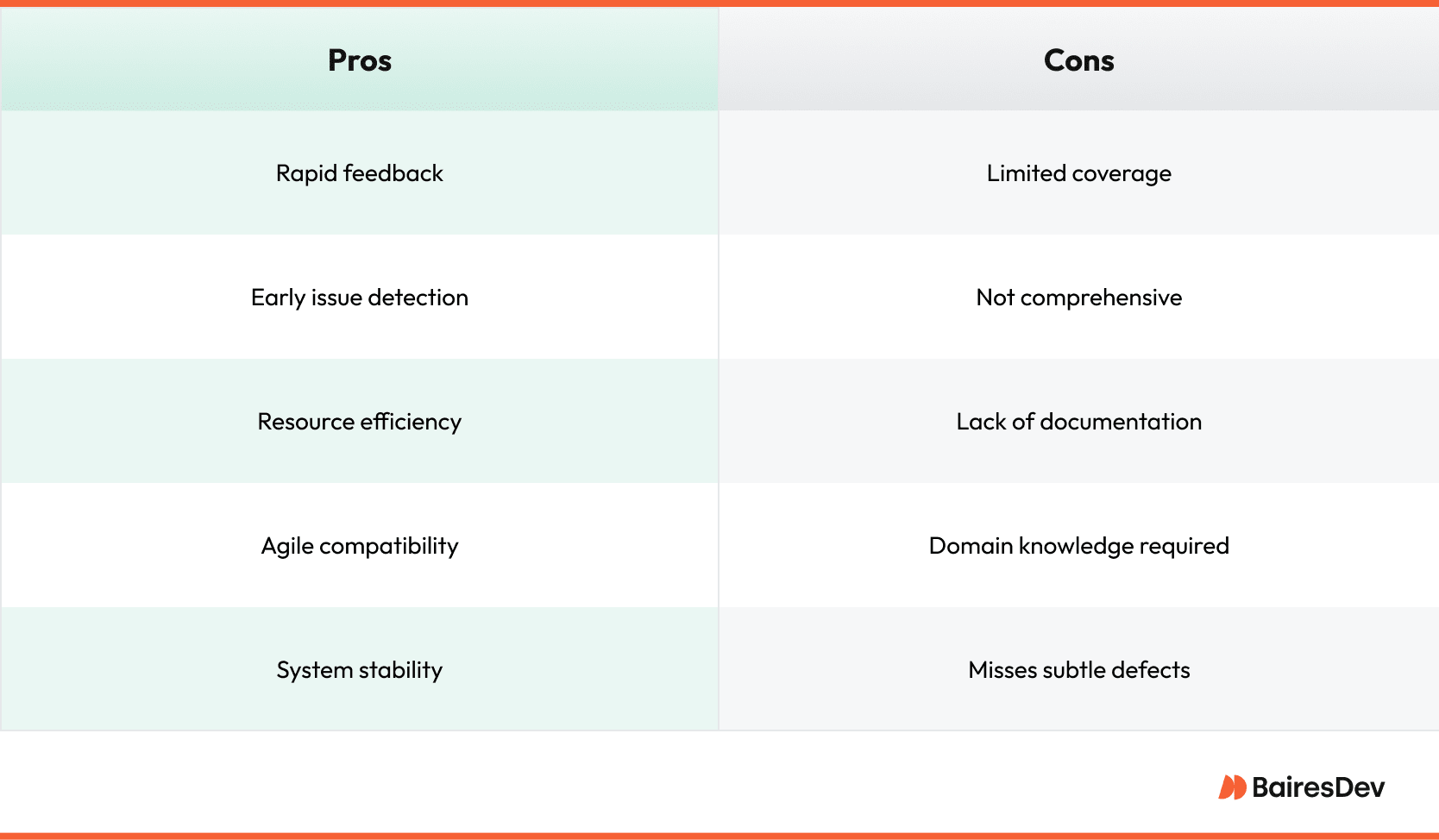
Rapid Feedback
Sanity tests quickly determine whether a software build, including new features or fixes, has disrupted existing functionalities. This leads to quicker insights. Rapid feedback can help ensure that a project adheres to its intended timeline.
Cost-Efficiency
The early detection of issues from a sanity test not only saves time—it also saves money. Verification testing, also known as build verification testing, helps in early detection of issues, ensuring that essential functionalities are operational, much like a health check-up for software. Fixing issues early on can prevent the need for costly fixes later in the development process.
Narrowed Focus
Sanity testing, often referred to as a quick sanity test, focuses on specific areas of functionality, ensuring they remain intact after changes. This preliminary testing can efficiently save time by identifying potential issues early in the development process, thereby facilitating timely action and planning for release progress. This narrowed focus ensures that each feature works as intended before you move on to more holistic testing.
Flexibility
Because of the non-scripted nature of sanity testing, testers have the liberty to choose their approach. Identifying major issues early in the testing process is crucial, as it ensures that unstable builds do not move forward to more extensive testing, thereby conserving time and resources. This means that there is plenty of room for flexibility and creativity in the testing environment.
Boosts Confidence for Releases
Successful sanity tests during the testing phase increase your team’s confidence in the software’s readiness for further testing or release. They improve clarity and collaboration and ensure that software is stable enough for the team to keep moving forward.
Optimal for Tight Deadlines
Because they are speedy, sanity tests serve as a basic test providing quick validations in time-sensitive projects, making them suitable in agile or tight-deadline scenarios.
Enhances User Experience
By ensuring core functionalities work as expected throughout the development cycle, testers can make sure that the user experience will be a positive one.
Software testing performed, such as sanity testing conducted after receiving a software build or after smoke testing, ensures that recent changes or bug fixes function correctly and do not introduce new defects.
Reduces Risks
Sanity testing ensures that the code change works correctly, preventing major issues from advancing to later stages in the development process. In other words, testers can resolve the issues before they get worse or cause more problems, thereby saving time and resources.
Drawbacks of Sanity Testing
Because sanity tests are not comprehensive, there are some drawbacks to them. Keep these sanity test drawbacks and testing best practices in mind.
Limited Coverage
Sanity testing is a quick and basic test that focuses on specific functionalities and sections of software. This potentially leaves other areas untested. It is important to understand that the purpose of sanity testing is not to check the entire system but to confirm that the system is ready for more exhaustive testing.
Not Comprehensive
Since sanity testing is narrow in its approach, it may not catch all potential issues, especially any bugs or errors that are outside of its defined scope. Complementing sanity testing with other testing methods ensures comprehensive coverage and helps maintain software quality during development. Being mindful of other potential issues and thinking outside the box can help testers ensure functionality.
Requires Expert Knowledge
Performing effective sanity testing often requires testers to have deep knowledge of the application. A regression test plays a crucial role in ensuring that changes do not introduce new issues. Testers need to quickly decide what to test based on any fixes or changes.
Not Suitable for Detailed Reporting
Sanity testing is typically undocumented. In-depth testing can follow sanity testing to provide detailed reports and logs. This means that it doesn’t involve detailed reports or logs, which can be a drawback for teams that require comprehensive documentation.
Conclusion
Sanity testing plays a crucial role in the software development process by providing rapid validation of specific functionalities, ensuring application stability. This type of testing ensures software stability so that testers can do more comprehensive testing with the confidence that the bugs and errors are cleaned up.
While sanity testing isn’t rigorous, it’s a quick way to assess and verify what needs to happen before exhaustive testing can happen. Overall, sanity testing helps streamline the bigger-picture testing process and ultimately improves the user experience.
FAQ
What is sanity testing?
A subset of regression testing, sanity testing is a crucial part of the software testing process that verifies certain functionalities still work correctly after minor fixes or alterations have been made to the software. It is typically a form of detailed testing, although its extent varies depending on factors like the project requirements and the changes that have occurred.
Regression testing is important for confirming and maintaining the software’s quality as you add new features, fix bugs, or make other changes.
What makes sanity testing different from comprehensive testing?
Sanity testing, unlike regression testing, differs from comprehensive testing in that it is narrow in approach. It focuses on specific functionalities instead of a system at large. The goal of sanity testing is to verify that specific features function as they should after a team makes any changes or modifications to the software. Once all functions are validated and any new bugs or issues are addressed, the team can move on to more comprehensive testing.
Are sanity tests always non-scripted?
Sanity tests are unscripted in nature to accommodate diverse and evolving testing needs, ensuring the application’s functionality operates as intended after minor code changes. This allows testers to be flexible and get creative in how they test features’ functions. However, project requirements and automation capabilities (or lack thereof) may change how teams test features.
What are different types of software testing?
There are many different types of software testing. Each type is aimed at assessing the reliability, functionality, performance, and/or security of software applications. Both sanity and smoke tests are designed to identify critical issues early in the testing process, ensuring that software builds are stable and that major functionalities are functioning as expected before proceeding to more extensive testing. There are basic and more rigorous testing phases, encompassing different approaches. As part of a comprehensive strategy, the development and testing team may perform unit, system, acceptance, regression, and integration testing. Other types include usability, compatibility, sanity, and smoke tests.






